Total
Session Time: 120 minutes + 2 hours visit to a
pharmacy store
Prerequisites
·
None
Learning
Tasks
By the end of this session students
are expected to be able to:
·
Define Medical Store
·
Describe Common Systems for
Arranging Medicines and Medical Supplies in the Store
·
Describe Common Equipment Used for
Medicines and Medical Supplies Storage
·
Describe Arrangement of Medicines
and Medical Supplies in the Store
Resources
Needed:
·
Flip charts, marker pens, and
masking tape
·
Black/white board, chalk and whiteboard
markers
·
LCD projector and computer
·
Handout 1.1 Arrangement and Organization of a
Store
·
Worksheet 1.1 Pictures of Store
Equipments
·
Field Trip Guide 1.1 A guide for a Visit to Hospital Pharmacy
Store
SESSION OVERVIEW
|
Step
|
Time
|
Activity/
Method
|
Content
|
|
1
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Introduction, Learning Tasks
|
|
2
|
10
minutes
|
Presentation Brainstorming
|
Definition of a Medical Store
|
|
3
|
20
minutes
|
Presentation
Buzzing
|
Common Systems for Arranging
Medicines and Medical Supplies
|
|
4
|
30
minutes
|
Presentation
Small
Group Discussion
|
Common Equipment Used in a Store
|
|
5
|
30
minutes
|
Presentation
Small
Group Discussion
|
Arrangement of Medicines and Medical
Supplies in the Store
|
|
6
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Key
Points
|
|
7
|
10
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Evaluation
|
|
8
|
10
minutes
|
Presentation
Visit
to a store
|
Pharmacy Store Visiting
|
SESSION
CONTENTS
STEP 1: Presentation of Session Title and Learning
Tasks (5 minutes)
READ or ASK students to read the learning tasks and clarify
ASK
students if they have any questions
before continuing.
STEP
2: Definition of a Medical Store (10 minutes)
|
Activity: Brainstorming (5 minutes)
ASK students to pair up and buzz on
the following question for 5 minutes
ALLOW few pairs to respond and let
other pairs to add on points not mentioned
WRITE their response on the flip
chart/board
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE by using the content below
|
- A medical store is a room where
medicines are kept under lock and key for the security and safety of
medicines and medical supplies.
- It is an area set aside into
which all the items and materials required for production,
sale/distribution are received, where they are housed for safekeeping, and
from which they will be issued as required.
- Also refers to a service
department headed by a store-keeper who is responsible for a proper
storage, protection and issuing of all kinds of material.
- The organization of the store
depend up on the size, layout of the factory, nature of the material
stored, frequency of purchases and issue of material
- The functions of a storekeeper
o To organize
medicines and medical supplies in a store and maintaining storage condition
o To keep and
maintain proper records of medicines and medical supplies
o To select
and determine items and quantities to be ordered as per requirements
o To receive
items in a store, arranging them properly and issue them as required
o Checking
expiry and proper disposal of unwanted items.
STEP 3: Common System for Arranging Medicines and
Medical Supplies (20 minutes)
|
Activity: Buzzing (5 minutes)
ASK students to pair up and buzz on
the following question for 10 minutes
- What
are the common systems used in arranging medicines and medical supplies?
ALLOW few pairs to respond and let
other pairs to add on points not mentioned
WRITE their responses on the flip
chart/board
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE by using the content below
|
·
The Common
Systems for Arranging Medicines and Medical Supplies includes:
- Alphabetical by generic
name: the medicines are arranged in the shelves according to their
alphabetical names, e.g. medicines starting with A- Albendazole,
Amoxicillin, Aminophylline, Ampicillin, with B- Bisacodyl, Bisoprol.
- Pharmacological/therapeutic: this is a classification or grouping of medicines with similar
pharmacological effects, for examples all Analgesics are grouped together,
or Anti-bacterial grouped together
- Dosage form: this is a system of classifying medicines based on dosage forms
used in stores, for example Tablets and capsules are stored together, a
separated area or location is reserved for say oral liquids, Injections,
creams and Ointments etc.
- Frequency of use: frequently used products that move quickly or often through the
store should be placed in the front of the room or closest to the staging
area. This system should be used in combination with another system
- Commodity coding: this system is based on
a unique article code combined with a unique location code. For example therapeutic
class/clinical indication in certain location name; MSD
Item is an example; 01300 7544 i.e.01300 item Code, and 7544
location code.
STEP 4:Common Equipment Used in Store (30 minutes)
|
Activity: Small Group Discussion (
15 minutes)
DIVIDE students into small manageable groups
ASK
students to discuss on the
following question
- What
are the common equipment used to store medicines and medical supplies in
a store?
 REFER students
to Worksheet 1.1: Pictures of
Store Equipments REFER students
to Worksheet 1.1: Pictures of
Store Equipments
ALLOW students to discuss for 15 minutes
ALLOW groups to present their opinions
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE
by using the contents below
|
·
Medicines/products are stored so
that they are easily accessible and protected against damage
·
The four basic equipment used for
storage are Shelves, Floor pallets, Block stacked pallets, and pallet racks.
§
Storage on shelves does not require
mechanical handling equipment and is a suitable choice when the volume and
weight of individual items are too small to justify pallets, the internal
height of a building is not large enough for multitier pallet racking and
shelving can be used on its own or in combination with floor pallets or
two-tier racking.
§
Manual goods handling is locally
more reliable or economical than mechanical handling.
§
If shelving is used in a warehouse
more than 4.5 meters high, it may be possible to install an independent
mezzanine flooring system supporting a second tier of shelving.
§
This can increase the available
shelving volume up to 100 percent, at the expense of some inconvenience in
material handling. Obliviously, if this is done, high –quality
construction is critical to avoid injury to staff and damage to stored goods.
§
Floor pallets are good solution in
warehouse with ceiling height of less than 3 meters and in store where the cost
of pallet racking and forklifts cannot be justified.
§
Many heavy or bulky items, such as
rolls of cotton, drug kits, or large hospital equipment, require floor
location.
§
Floors should be marked to indicate
pallet and aisle position.
§
Pallets containing light goods may
be stacked on top of one another in blocks.
§
Blocks-stacked pallets should be
used only for items without expiry dates or with very high turnover, because
the first-in terms are the bottom of the stack.
§
Block stacking is a cheap and space
efficient method of storage and no racking is required
§
Simple pallets racks generally have
two or three tiers.
§
Two tiers of racking require a clear
height of about 3 meters, and three ties require a clear height of about 4.5
meters
§
It is possible to have several more
tiers to have several more tiers but sophisticated mechanical handling
equipment is then required
STEP 5: Arrangement of Medicines and Medical Supplies
in the Store (30 minutes)
|
Activity: Small Group Discussion (
10 minutes)
DIVIDE students into small manageable groups
ASK
students to discuss on the
following question
- How
do you arrange medicines and medical supplies in a store?
ALLOW students to discuss for 10 minutes
ALLOW groups to present their opinions
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE
by using the contents below
|
·
Supplies should be arranged
according to:
o
First expiry/first out (FEFO)
§
Supplies which expire first should
be in front and be issued first in preference to those with longer expiry dates
o
First in first out (FIFO),
§
Always issue first those medicines
which have been in the store the longest
§
Place newly received items on the
shelves or pallets so that those present automatically move to the front and
are issued first
§
This applies especially for drugs
with none expiry dates
o
Category or formulation
o
In alphabetical order
 Refer
students to Handout 1.1: Arrangement and Organization for further reading.
Refer
students to Handout 1.1: Arrangement and Organization for further reading.
STEP 6: Key Points (5 minutes)
·
A medical store is a room where
medicines are kept under lock and key for the security and safety of medicines
and medical supplies
·
The functions of a store keeper is
to organize and maintain storage conditions, keeping records and maintain
availability of medicines to store
·
Common systems for arranging medicines and medical
supplies in a store includes, alphabetical by generic name,
pharmacological/therapeutic, dosage form, frequency of use, random bin and
·
The four basic equipment of storage of medicine and
medical supplies are, Shelves, Floor pallets, Block stacked pallets, and pallet
racks.
STEP 7: Evaluation (10 minutes)
·
What is a medical store?
·
What are
the common systems used in arranging medicines and medical supplies?
·
What equipment are used to store
medicine and medical supplies in a storeHow do you arrange medicines and
medical supplies in the store?
STEP 8: Visit to a Store (10 minutes)
|
Activity: Visit to a store (120
minutes)
PREPARE
for a visit to a hospital store
ORIENT
the students on objectives and
guide of the visit
 REFER students
to Field Trip Guide 1.1: A Guide
for a Visit to Hospital Pharmacy Store REFER students
to Field Trip Guide 1.1: A Guide
for a Visit to Hospital Pharmacy Store
DIVIDE
students to manageable small
groups
TAKE
students to the site to learn
about pharmacy store arrangement.
PREPARE
students for feedback of the visit
|
References:
Jessop, D and Morrison (1994) Storage and Supply of Materials, (6th
ed.), Prentice Hall
Laurie L, Editor, (2003) Guidelines
for the Storage of Essential Medicines and Other Health Commodities. John Snow,
Inc./DELIVER in collaboration with the World Health Organization
Management Science
for Health and World Health Organization. (1997). Managing Drug Supply, (2nd ed.).West Hartford, Connecticut, USA:
Kumarian Press
Management Science for Health and World Health Organization.
(2012). Managing Access to Medicines and Health Technology, (3rd ed.). Kumarian
Press
Shirima, L. L (1988): Basic
Store-keeping and Warehouse Management. General Publication
World Health Organization (WHO), Regional Office for Africa
Brazzaville 2004, Management of Drugs
at Health Centre Level Training Manual.

|
Handout 1.1: Arrangement and
Organization of a Store
|
Proper Arrangement and Organization`
Requirements for Proper Arrangement
·
Storage area or the store should be
clean
·
Must be arranged in an orderly
manner so that each item is easily accessible
·
Supplies should be stored according
to manufacturer’s storage requirements (e.g. light, temperature and
humidity)
·
Medicines in store rooms are
arranged according to the specified management principles of the organization
·
Drugs and medical supplies must be
properly stored in order to maintain their stability and quality up to the end
of their stated time of use
Classification of Drugs in the Store
·
Medicines are also grouped according
to the pharmacological classification; this provides a useful reference point
with which a health worker can easily recognize individual products
·
Put frequently used items at waist
height
·
Store extra stock on upper shelves
(if not too heavy)
·
Top shelf should be used to store
dry medicines (tablets, capsules, oral rehydration packets)
- If the top shelf is near the
ceiling or out of your reach, use that shelf to store items that are NOT
sensitive to heat and are NOT used regularly
·
Middle shelf should be used to store
injectable and ointments
·
However, note that liquids and
syrups can also be stored but with caution as they can leak
·
Lower shelves can be used to store
other supplies, such as surgical items, laboratory supplies and condoms
·
Level of use (i.e. for fast moving
medicines) must be placed where they are easy to reach
·
Labels for product name can be put
on shelves where that item is located for easy access
·
Consider the labels on the items
carefully, these indicate the storage requirements
·
The store should be located in a
place that is not easily reached by flooding
·
It should be accessible to transport
and secured from theft and fire
Storage and Use Procedures
·
All stock should be checked for
expiration dates at regular intervals (monthly)
·
Items with shorter expiration dates
should be issued first (FIFO)
·
Reduce waste caused by drug
expiration by sharing with the nearby facilities (this must be agreed with the
Hospital Therapeutic Committee)
- Note: Items should never be
placed on the floor.

|
Worksheet 1.1: Pictures of Store
Equipments
|

|
Field Trip Guide 1.1: A guide for a Visit to Hospital
Pharmacy Store
|
Introduction
This guide will help a student to
understand better on common system for arranging medicines and medical supplies
in a store also to build more capacity on how to arrange medicines and medical
supplies in a store by visiting to a hospital pharmacy store and observe by
visualizing what is real done by store workers.
Student should be divided into small
group may be of 5 to 10 members to simplify managing them once they are passing
from one area of studying to another within a store.
Each group should have a Chairman, a
recorder and a reporter
Learning
Tasks
·
Identify common system for arranging
medicines and medical supplies
·
Identify arrangement of medicines
and medical supplies in the store
Activity
·
Students to prepare themselves by
having important tools like pen, notebook, overall coat, boots and any other
related material for the visit
·
Locate four basic arrangement of
storage: Shelves, Floor pallets, Block stacked pallets, and pallet racks.
·
Observe common system for arranging
medicines and medical supplies
·
Observe arrangement of medicines and
medical supplies in the store
At the end of this activity the
groups of students will submit a report of what they have learned from this
study tour of a hospital pharmacy store
Each group will present their
learning experiences in the class.
A facilitator will summarize and
make more elaboration on important issue
Total
Session Time: 120 minutes
Prerequisites
·
None
Learning Tasks
By the end of this session students
are expected to be able to:
·
Keep records of
medicines and medical supplies
- Define
Medicines and Medical Supplies Records
- List
Records of Medicines and Medical Supplies
- Explain
the Importance of Records of Medicines and Medical Supplies
- Demonstrate
Ability to Record and Keep Medicines and Medical Supplies
Resources
Needed:
·
Flip charts, marker pens, and masking tape
·
Black/white board, chalk and whiteboard
markers
·
LCD projector and computer
·
Ledger, Bin Card, Issue voucher,
Receipt voucher, and Requisition forms
·
Handout 2.1: Records of medicines and medical
supplies
·
Figure
2.1: Samples of medicines and medical supplies
records
SESSION OVERVIEW
|
Step
|
Time
|
Activity/
Method
|
Content
|
|
1
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Introduction, Learning Tasks
|
|
2
|
10
minutes
|
Presentation
Buzzing
|
Definition of Medicines and
Medical Supplies Records
|
|
3
|
15
minutes
|
Presentation Brainstorming
|
Records of Medicines and Medical
Supplies
|
|
4
|
20
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Importance of Medicines and
Medical Supplies Records
|
|
5
|
60
minutes
|
Presentation
Small
Group discussion
|
Recording
and Keeping Medicines and Medical Supplies
|
|
6
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Key
Points
|
|
7
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Evaluation
|
SESSION
CONTENTS
STEP1:
Introduction, Learning Tasks (5 minutes)
READ or ASK students to read the learning tasks and clarify
ASK
students if they have any questions
before continuing
STEP 2: Definition
of Medicines and Medical Supplies Records (10 minutes)
|
Activity: Buzzing (5 minutes)
Ask students to pair up and buzz on
the following question for 2 minutes:
- What
is medicines and medical supplies records?
ALLOW few students to respond
WRITE their responses on the flip
chart/ board
CLARIFY and SUMMARISE by using the content below
|
Medicine and medical supplies records
·
Is the records which
contain important information concerning:
- What items are available
- How much is available of each item
- How much is used on a regular basis
- When and how much of an item should be
reordered
·
They are used to record
information about medicines and medical supplies in storage.
·
They must contain the
quantity of medicines and medical supplies on hand; the quantity of losses; and
the quantity of adjustments, by individual product.
·
The medicines and
medical supplies records are completed by anyone who receives or issues stock
from storage, and by anyone who takes a physical count of medicines and medical
supplies in stock, service delivery point (SDP) staff.
STEP
3: Records of Medicines and Medical
Supplies (15 minutes)
|
Activity: Brainstorming (5 minutes)
ASK students to brainstorm on the
following question:
- What
are the records for medicines and medical supplies?
ALLOW few pairs to respond and let
other pairs to add on points not mentioned
WRITE their response on the flip
chart/board
`
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE by using the content below
|
·
Records
for medicines and Medical supplies
- Store Ledger
- Bin Cards
- Issue voucher
- Receipt voucher
- Requisition form
·
Stores ledger
o
Stores
ledger is a stock keeping record forms bound like a book that containing the
information about the products regarding quantities in the store.
o
It
also records dates and quantities from who received into the store as well as
quantities to whom issued from the store.
o
It
is a legal document used by auditors, stock-verifiers to assess validity of
stocks.
o
The
Government policy in most countries requires the use of stores ledgers for
accountability , because commodities are considered assets of the
government or organizations and should
be accounted for carefully
·
Bin Card
o It is an
individual stock keeping record that holds information about all the
lots of a single product.
o One Bin Card is
for each product
·
Issue
vouchers
o Issue vouchers are used where the
issuing facility determines the quantity to be sent and issues the supplies to
the receiving facility.
·
Receipt
voucher
o A Receipt Voucher
lists the items and quantity issued from supplier and received by a facility.
o It also includes a
separate column for the quantities received in case any items are lots or
damaged en route
o The issuing
facility completes the date and quantities issued, signs the voucher
·
Requisition
forms/
vouchers
o A requisition
voucher is completed by facility staff by listing the items and quantities
requested by a facility.
o It also includes a
column for the quantity actually issued.
 REFER students to
Handout 2.1: Records of Medicines and Medical supplies for further reading.
REFER students to
Handout 2.1: Records of Medicines and Medical supplies for further reading.
STEP 4: Importance
of Medicine and Medical Supplies Records (20 minutes)
- Importance of Medicine and medical supplies records
are:
o
They reflect/show quantities of the
items at the store ( stock in hand )
o
They protect the store keeper from
rumours of misuses or fraud of the medicines and medical supplies in the store.
o
They provide information on the consumption
rate, for deciding what to order and the quantity to order.
o
They are used for accountability of
medicines and medical supplies regarding quantities received, issued and to
whom they were issued.
o
They indicate the value of assets of an institution
o
They are used as legal requirement for accountability
during auditing, stock verification.
o
They are also required by professional bodies like
pharmacy council, for accountability of sources and movement of medicines and
medical supplies ( legal sources and uses)
STEP 5: Recording
and Keeping Medicines and Medical supplies (60 minutes)
|
Activity: Small Group Discussion (
30 minutes)
DIVIDE students into small manageable groups
ASK
students to discuss on the
following question
·
What is the
most important reasons for having stock keeping records?
ALLOW students to discuss for 30 minutes
ALLOW few groups to present and the rest to add points not mentioned
 REFER students to Hand Out 2.1 for further reading. REFER students to Hand Out 2.1 for further reading.
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE
by using the contents below
|
STEP 6: Key Points (5 minutes)
·
Records contain important
information which are used to record information about medicines and medical
supplies in a store.
·
Records
for medicines and Medical supplies include Store Ledger, Bin Cards, Issue
voucher, Receipt voucher, Requisition form.
·
It is
important to ensure that all medicines and medical supplies kept in the store
to be recorded
STEP
7: Evaluation (5 minutes)
·
What is medicines and medical
supplies records?
·
What are the records for medicines
and medical supplies?
·
What are the importance of records
of medicines and medical supplies?
References
Management Science for Health and World Health Organization.
(2012). Managing Access to Medicines and
Health Technology, (3rd ed.). Kumarian Press
Management Science for Health and World Health Organization.
(1997). Managing Drug Supply, (2nd
ed.).West Hartford, Connecticut, USA: Kumarian Press
World Health Organization (WHO), Regional Office for Africa
Brazzaville 2004, Management of Drugs
at Health Centre Level Training Manual
Shirima, L. L (1988): Basic Store-keeping and Warehouse
Management. General Publication United Republic of Tanzania, Public Procurement Act, 2004, Dar es
Salaam
Jessop, D & Morrison (1994) Storage and Supply of Materials, (6th
ed.). Prentice Hall
Laurie L, Editor, (2003) Guidelines
for the Storage of Essential Medicines and Other Health Commodities. John Snow,
Inc. /DELIVER in collaboration with the World Health Organization

|
Handout
2.1: Records of Medicines and
Medical Supplies
|
|
What is the most important reason for having stock
keeping records?
They are used to record
information about products in storage.
What essential data items do stock keeping records
contain?
They must contain the quantity of stock on hand; the
quantity of losses; and the quantity of adjustments, by individual product.
Who completes the stock keeping record?
It is completed by anyone who
receives or issues stock from storage, and by anyone who takes a physical
inventory of the stock, including the warehouse manager and other warehouse
staff, and service delivery point (SDP) staff. Pharmacies store stock; the
staff should also use stock keeping records. The pharmacist and other
pharmacy staff are responsible for completing these stock keeping records.
When are entries made to stock keeping records?
They
are recorded on the stock keeping record whenever products are received or
issued. Entries are also recorded when stock is counted during a physical
inventory, or as soon as a loss is noticed. When the stock keeping record is
full, a new record is started, using the ending balance from the previous
record.
How are the data on a stock keeping record
organized?
They are organized by date and
transaction reference (the unique number of the corresponding transaction
record for a receipt or issue, and/or the name of the facility from which
products are received and issued). They record receipts, issues, losses and
adjustments, and the balance on hand. They also record the results of physical
inventories (when items are counted to verify the quantity in storage).
What are some examples of formats of stock keeping
records?
The
most common formats for stock keeping records are individual stock cards and
stores ledgers. Types of stock keeping records include stock cards, inventory
control cards, and bin cards.
What is a bin card?
It is an individual stock keeping record that holds
information about a single product by lot number or batch number (see figure
2-2). Every item in that lot will have the same expiration date. For example,
one bin card would hold information about a single lot of paracetamol at a
storage facility. The card should note the stock on hand of paracetamol for
that lot only, as well as any losses and adjustments for that lot. Bin cards
are usually displayed at the bins (or shelf or pallet position) where the lot
is found.
What is a stores ledger?
It is
a stock keeping record that contains the same information as the inventory
control card described above. Unlike inventory control cards, a stores ledger
is bound like a book; it is used instead of the individual card format.
Government policy in some countries requires the use of stores ledgers.
(Managers may think that binding the pages increases accountability, because
missing pages are obvious.) However, the ledger format is less desirable than
individual cards, because it is easy to run out of space for an individual
product. It is also hard to add new products—you can alphabetize a set
of individual inventory control cards as new cards are added, but you cannot
alphabetize pages within a bound book. In many countries, the format of stock
keeping records is determined by the Ministry of Finance and is used by all
government units because commodities are considered assets of the government
and should be accounted for carefully.
What is an inventory control card?
It is
an individual stock keeping record that holds information about all the
lots of a single product. You should keep one inventory control card for each
product. The inventory control card may be a summary of many bin cards for a
particular product. For example, one inventory control card could hold
information about all the paracetamol in a storage facility. It should note
the total stock on hand of paracetamol in the warehouse, as well as the total
losses and adjustments, without regard to lot number or where the product is
located in the warehouse. See figure 2-3 for an example of an inventory
control card. To ensure that each lot is managed correctly in larger
warehouses, which may have many lots of each product stored in different
places, it is usually advisable to maintain both inventory control cards and
bin cards. In smaller storerooms, you can keep a single stock keeping record,
such as a stock card or inventory control card.
How and where do stock-keeping
records move?
Stock-keeping
records do not usually
move; they stay where products are stored (e.g., the warehouse, pharmacy, or
storeroom).
What are some examples of
formats for transaction records?
The most common formats are
bills of lading; receiving records; issue vouchers; receipt vouchers; and
combined requisition, issue, and receipt vouchers. The content of the
transaction record will depend on how many transactions and which parts of
the transaction are tracked on the record. The format of the transaction
record may also depend on whether the system is pull or push. In all cases, a
preprinted voucher number on each transaction record helps track individual
shipments.
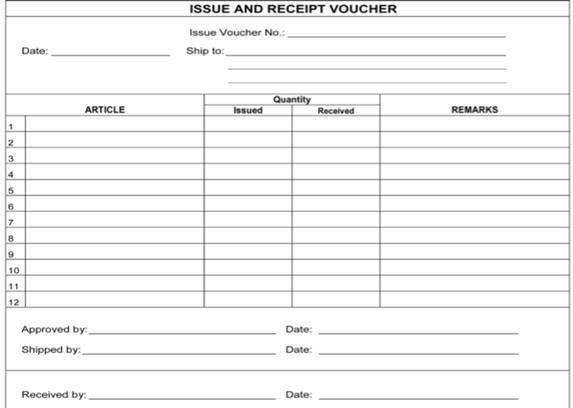
What is an issue and receipt voucher (IRV)?
An IRV
lists the items and quantity issued to a facility. It also includes a
separate column for the quantities received in case any items are lots or
damaged en route. IRVs are used in a push system; the issuing facility
determines the quantity to be sent and issues the supplies to the receiving
facility.
Figure 2.1: Samples of Medicines and Medical Stores
Records
·
Store ledger
o The
Stores Ledger is a register for recording movements of stock kept in the
facility. It is used to record receipts and issues of stock.
·
Requirements
o
It MUST be kept up to date
o
Separate Stores Ledgers should be kept for
pharmaceutical supplies and non-pharmaceutical supplies.
·
How to fill a store
ledger
o Record
immediately, (i.e. without delay), every receipt or issue of stock. Records
for every item MUST be on a separate page in the ledger. Supplies should be
differentiated by generic name (Panadol vs. Paracetamol),The strength of the
product (e.g., Amoxicillin 500mg), The form (e.g., Tablet, suspension).Example
Amoxicillin Capsules 250mg.
o A consistent unit of issue must be applied
to all entries in the ledger. Record entries by the dispensing unit instead
of pack sizes. All supplies must be entered in alphabetical order for the
supplies in a single storage area within the facility.
o Each
ledger should start with a table of contents page that will help to find the
product page quickly.
o Write
page numbers of the ledger. When the page in use is full, indicate on this
page as to which page you have transferred the data and indicate on the new
page as from where the information has been transferred.
STORE LEGDER SAMPLE
FACILITY CODE NUMBER:
………………………………..
FACILITY NAME
…………………………………….............
TYPE OF FACILITY (GOV/NGO/FBO/OTHER)
……………
NAME OF COUNCIL /REGION
…………………………….
DATE LEDGER BOOK
OPENED……………………………..
DATE LEDGER BOOK
CLOSED………………………….....
·
Bin card
o It
is an individual stock keeping documentation tool that holds information
about a single product by lot number or batch number. Every item of the lot
have the same expiration date.
o For
example, one bin card would hold information about a 500mg paracetamol tablet
at a storage facility. The card note the stock on hand of paracetamol for
that strength only, as well as any losses and adjustments.
o Bin
cards are usually displayed at the bins (or shelf or pallet position) where
the lot is found
·
Items
on a stock card/bin-card include:
- DATE
when item is received into store or issued out of store
- RECEIVED
FROM (usually MSD)
- QUANTITY
RECEIVED (number of units received at store)
- ISSUED
TO (name of patient to whom the item will be dispensed)
- QUANTITY
ISSUED (number of units issued out of store)
- ADJUSTMENT
(number of unit expired ,lost/stolen)
- BALANCE
IN STOCK (number of units remaining in store)
- REMARKS Important information about movement of item, batch
numbers, expiration dates,
borrowed from or returned to other health
facility etc.
- SIGNATURE of the person who records the movement of the
item
Note: During
practicum session students should fill/complete stores ledger, Bin cards,
R&R and Requisition/issue voucher.
·
Issue and receipt voucher ( IRV )
o An IRV lists the items and
quantity issued to a facility. It also includes a column for the quantities
received in case any items are lost or damaged.
o IRVs are used in a push
system/kit system where the issuing facility determines the quantity to
be sent and issues the supplies to the receiving facility. An IRV should be
completed in triplicate (three copies).
IRV flow between facilities
The
issuing facility completes the date and quantities issued, signs the voucher,
and sends the top two copies (1 and 2) to the receiving facility, with the
supplies.
The
bottom copy (3) is often called the reminder copy because the issuing
facility keeps the bottom copy of the issue voucher as a reminder that it is
waiting for verification that the supplies were received.
Step
two.
The
receiving facility verifies the quantity received, signs the form, and
returns the top copy (1), and keeps the middle copy (2) for its files.
Step
three
The
top copy (1) arrives at the issuing facility, which then disposes of the
reminder copy (3) and keeps the top copy for its files and thus each of the
facilities will have a completed copy.
|
|
|
|
Total
Session Time: 120 minutes
Prerequisites
·
None
Learning
Tasks
By the end of this session students are expected to be able to:
·
Define
Housekeeping of Medicines and Medical Supplies Store
·
Describe
Housekeeping Tasks for Store
·
Explain
the Importance of Housekeeping in the Store
·
Explain
the consequences of Poor Housing Keeping
Resources
Needed:
·
Flip charts, marker pens, and
masking tape
·
Black/white board, chalk and whiteboard
markers
·
LCD projector and computer
SESSION OVERVIEW
|
Step
|
Time
|
Activity/
Method
|
Content
|
|
1
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Introduction, Learning Tasks
|
|
2
|
10
minutes
|
Presentation
Brainstorming
|
Definition
of Housekeeping of Medicines and Medical Supplies Store
|
|
3
|
45
minutes
|
Presentation
Small
group discussion
|
Description
of Housekeeping Tasks in Medicine and Medical Supplies
Store
|
|
4
|
25
minutes
|
Presentation
Buzzing
|
Importance of Housekeeping in
Medicines and Medical Supplies Store
|
|
5
|
25
minutes
|
Presentation
Buzzing
|
Consequences of Poor Housing Keeping
in Medicines and Medical Supplies store
|
|
6
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Key
Points
|
|
7
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Evaluation
|
SESSION
CONTENTS
STEP1:
Introduction, Learning tasks (5 minutes)
READ or ASK students to read the learning tasks and clarify
ASK
students if they have any questions
before continuing
STEP 2: Definition
of Housekeeping of Medicines and Medical Supplies Store (10 minutes)
|
Activity: Brainstorming (5 minutes)
ASK students to brainstorm on the
following question:
- What
is housekeeping of Medicines and Medical Supplies store?
ALLOW few pairs to respond and let
other pairs to add on points not mentioned
WRITE their response on the flip
chart/board
`
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE by using the content below
|
o This is the tasks in a store which
include the following activities cleaning, pest control, a regular inspection
system, disposal of stock, precaution against fire, and strict security
measures.
STEP 3: Description of Housekeeping Tasks in Medicines
and Medical
Supplies Store (45 minutes)
|
Activity: Small Group Discussion (
20 minutes)
DIVIDE students into small manageable groups
ASK
students to discuss on the
following question
·
What are
housekeeping tasks in Medicines and Medical Supplies store?
ALLOW students to discuss for 20 minutes
ALLOW few groups to present and the rest to add points not mentioned
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE
by using the contents below
|
·
Cleaning
and pest control
- The store should be kept tidy and should be
cleaned two or three times a week.
- Pest control can be difficult task, but to
avoid possible contamination and physical damage to stock.
- It’s necessary to keep insect, mice and
other pests out of the storage area. If needed, pest control measure such
as poison should be implemented with proper precaution.
·
Inspection
- Senior staff should inspect the store
regularly. The chief storekeeper must make sure that store room employees
check the shelves and pallets daily and for deterioration due to climatic
condition. Store keepers should open suspect containers and reports
problems to managers.
·
Disposal
of expired or damaged stock
- Damaged or expired stock should be placed in a designated
salvage area to wait authority for disposal. A written record of all stock
consigned to this area should be maintained. It’s recommended that
each item be valued at its acquisition cost. The responsible authority
should be informed in writing that stock is to be written off. Disposal
may be delayed if a committee decision is required, and substantial
storage space and May needed for junk stock. Once destruction is
authorized, the inventory control clerk must adjust the stock records. All
drugs and other potentially toxic products should be disposed of in
accordance with local regulation in a manner that does not pose not pose a
risk to public health.
·
Fire
precaution
- Flammable trash, such as cartons and boxes,
must not be allowed to accumulate in the store. Smoking must be strictly
forbidden, with “No smoking” signs posted throughout the store.
Senior staff must obey the rule as strictly as junior staff, and penalties
should be imposed on these who ignore the rules. A smoking area outside
the warehouse should be designated. Management must ensure that
fire-detection and fire-fighting equipment is regularly inspected and that
staff receive adequate training in fire -fighting technique and emergency
action. There should be regular
fire drills to reinforce the training.
·
Security
- Ideally, the chief storekeeper’s office
should have windows that overlook the loading bay, the compound entrance,
and the store itself. A storekeeper who sits behind a closed door with
curtains drawn cannot observe what is happening on the site. No vehicles
should be allowed into the store compound unless they are authorized by
the chief storekeeper or senior staff member. A list of authorized
vehicles should be prepared for the compound gate-keeper.
STEP 4: Importance
of Housekeeping in the Store (25 minutes)
|
Activity: Buzzing (5 minutes)
ASK students to pair up and buzz on
the following question for 5 minutes
- What
are the importances of housekeeping in Medicines and Medical Supplies
store?
ALLOW few pairs to respond and let
other pairs to add on points not mentioned
WRITE their response on the flip
chart/board
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE by using the content below
|
·
The following are the importance of housekeeping in
the store
- Promotes quality safety productivity
- Decreases fire hazards
- Makes the store looks neat and orderly and eases
flow of drug and supplies
- Improves
morale among workers
- Better
control of drugs and supplies, including inventory maintenance
- Better
hygienic conditions leading to improved health
- More
effective use of space
- Reduces
drug and supplies damage
- Reduces
tripping and slipping accidents in clutter-free and spill-free work areas
- Minimize workers exposures to hazardous
substances (e.g. dusts, vapors)
STEP 5: Consequences of Poor Housing keeping (25
minutes)
|
Activity: Buzzing (10 minutes)
ASK students to pair up and buzz on
the following question for 10 minutes
- What
are the consequences of poor housekeeping in Medicines and Medical
Supplies store?
ALLOW few pairs to respond and let
other pairs to add on points not mentioned
WRITE their response on the flip
chart/board
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE by using the content below
|
·
The followings are the consequence of poor house
keeping
o
Injuries, when employees trip, fall, strike or are
struck by out-of-place objects
o
Makes the store looks untidy and messy
o
Time consuming when picking item from a poorly
arranged store
o
Fire due to improper storage of inflammable or
combustible materials and wastes
o
Risk of medicine deterioration as may be subjected to
unfavourable conditions
o
Compromise workers efficiency due to unconducive environment
STEP 6: Key Points (5 minutes)
·
Housekeeping
tasks in a store include cleaning, pest control, a regular inspection system,
disposal of stock, precaution against fire, and strict security measures.
·
Importance
of housekeeping in medicines and medical supplies include promotion of quality safety production, decreases fire
hazards and makes the store looks neat and orderly and eases flow of drug and
supplies
·
Consequences
of poor housing keeping include Injuries, when employees
trip, fall, strike or are struck by out-of-place objects
STEP 7: Evaluation (5 minutes)
- What
is housekeeping of medicines and medical supplies store?
- What
are the housekeeping tasks in medicines
and medical supplies store?
- What
are the importance of housekeeping in medicines and medical supplies
store?
- What
are the consequences of poor housekeeping in medicines and medical
supplies store?
References
Management Science for Health and World Health Organization.
(2012). Managing Access to Medicines and
Health Technology, (3rd ed.). Kumarian Press
Management Science for Health and World Health Organization.
(1997). Managing Drug Supply, (2nd
ed.).West Hartford, Connecticut, USA: Kumarian Press
World Health Organization (WHO), Regional Office for Africa
Brazzaville 2004, Management of Drugs
at Health Centre Level Training Manual.
Shirima, L. L (1988): Basic Store-keeping and Warehouse Management.
General Publication
Jessop, D and Morrison (1994) Storage and Supply of Materials,
6th Edition, Prentice Hall
Laurie L, Editor, (2003) Guidelines
for the Storage of Essential Medicines and Other Health Commodities. John Snow,
Inc. /DELIVER in collaboration with the World Health Organization
Total
Session Time: 120minutes
Prerequisites
·
None
Learning
Tasks
By the end of this session students
are expected to be able to:
·
Define Issuing of Medicines and
Medical Supplies From a Store
·
Identify the Documents Used for
Issuing Medicines and Medical Supplies From a Store.
·
Explain the Procedure for Issuing
of Medicines and Medical Supplies
·
Filling
Documents Used in Issuing Medicines and Medical Supplies
Resources
Needed:
·
Flip charts, marker pens, and
masking tape
·
Black/white board, chalk and whiteboard markers
·
LCD projector and computer
·
Worksheet 4.1
Issue voucher
·
Worksheet 4.2
Issue voucher
SESSION OVERVIEW
|
Step
|
Time
|
Activity/
Method
|
Content
|
|
1
|
5
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Introduction, Learning Task
|
|
2
|
10
minutes
|
Presentation
Brainstorming
|
Definition of Issuing Medicines
and Medical Supplies From a Store
|
|
3
|
15
minutes
|
presentation
|
Documents Used for Issuing
Medicines and Medical Supplies From a Store.
|
|
4
|
30
minutes
|
presentation
|
Procedure for Issuing of Medicines
and Medical Supplies
|
|
5
|
50
minutes
|
Presentation
Small
group discussion
|
Filling Documents Used in Issuing
Medicines and Medical Supplies
|
|
6
|
5
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Key
Points
|
|
7
|
5
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Evaluation
|
SESSION
CONTENTS
STEP1:
Introduction, Learning tasks (5minutes)
READ or ASK students to read the learning tasks and clarify
ASK
students if they have any questions
before continuing
STEP 2: Definition of Issuing Medicines and Medical
Supplies From a Store
(10minutes)
|
Activity: Brainstorming (5 minutes)
ASK students to pair up and buzz on
the following question for 5 minutes
- What
is issuing medicine from a store?
ALLOW few pairs to respond and let
other pairs to add on points not mentioned
WRITE their response on the flip
chart/board
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE by using the content below
|
·
Issuing of medicines from a store
- Issuing of medicine from a store is the process
of distributing a specific amount of an item from store to different
department of the health facility.
·
STEP 3:
Documents Used for Issuing Medicines From a Store(30 minutes)
·
Document
that is common used in health facility for issuing medicines from a store is
issue voucher.
·
Issue
voucher is a document used when you issue items to another health unit or to
department in your unit. It records :
o
The date of issue
o
The item requested and quantity
o
The items issued and quantity
o
The department receiving
o
Signature of the receiver and issuing officer
·
STEP 4:
Procedure for Issuing of Medicines and Medical Supplies
(30 minutes)
·
Medicines
and related supplies should be issued within or moved out of the facility by
following agreed procedure
- Requisition
officer has to identify requirement of needed supplies
- Requisition
has to be clearly written on the standard requisition form
- On reaching
the store, the requisition has to be examined by a store keeper and any
necessary change made and initialed.
- Store
keeper should issue the supplies accordingly.
- The
assembled order has to be checked by the storekeeper.
- All records
should be documented on bin card and ledger book with all necessary
details completed on the same date.
- Types, name
and quantity of the required items, signature of the receiving and issuing
officer and the date should appear on the issue voucher.
- Store
keeper has to ensure proper handling of the supplies to requisition
officer.
STEP 5: Filling Documents Used in Issuing Medicines
and Medical Supplies
(50 minutes)
|
Activity: Small Group Discussion (
30 minutes)
DIVIDE students into small manageable groups
ASK
students to discuss on the
following question
·
How to fill
issue voucher used in issuing medicines and medical supplies?
ALLOW students to discuss for 30 minutes
ALLOW few groups to present and the rest to add points not mentioned
 REFER students to work sheet 1 and 2 for further reading. REFER students to work sheet 1 and 2 for further reading.
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE
by using the contents below
|
·
Filling
documents used in issuing medicines and medical supplies require a trained
personnel
·
The
following below documents shall be filled as follows
§ Write the full
name, designation and official signature of the person requesting supplies.
§ Write the
numbers of items requested in sequence order.
§ Write generic
name of the product, strength and dosage form e.g. Paracetamol tablet 500mg
§ Write unit of
measure of item ( pack size )
§ Write the
quantity of the items required
§ Write the
quantity of item to be supplied out of store
§ Write important
information about movement of item, batch numbers, expiration dates, borrowed
from or returned to other health facility.
§ Write the date
when the supplies were issued.
§ Write
designation and signature of the issuing officer.
NOTE. The line shall be drawn below
the last item to be issued to avoid tempering.
STEP 6: Key Points (5minutes)
·
Issuing of medicine from a store is the process of
distributing a specific amount of an item from store to different department of
the health facility.
·
Document
which is common used in health facility for issuing medicines from a store is
issue voucher.
·
One of the Procedures for issuing
of medicines and medical supplies include identifying the correct quantity
required to be supplied.
·
Documents
used in issuing medicines and medical supplies shall be properly filled with
generic name, quantity of the required items, signature of the receiving and
issuing officer and the date on the issue voucher.
STEP 7: Evaluation (5 minutes)
·
What is issuing of medicines and
medical supplies from a store?
·
What are the documents used for
issuing medicines from a store?
·
What are the important procedures
for issuing of medicines and medical supplies?
References
Ministry of Health and Social
Welfare (MOHSW). Modular course in district health management: module 7. Dar es
salaam TZ. Ministry of Health and Social Welfare.
Guidelines on the storage of
essential drug in eastern and southern Africa (1991) by WHO with the
cooperation of the pharmaceutical industry through the International Federation
of Pharmaceutical Association IFPMA
Management Science for Health and World Health Organization.
(1997). Managing Drug Supply, (2nd
e.d.).West Hartford, Connecticut, USA: Kumarian Press

|
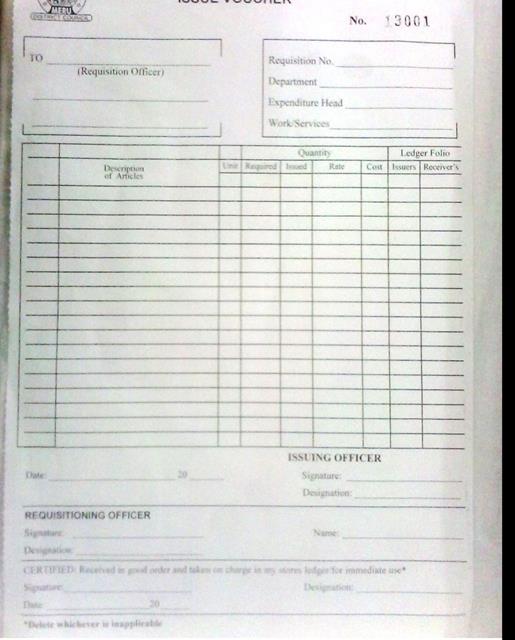
Worksheet4.1: Issue Voucher
|
|
Instructions
: verifying the content of the issuing document and keep record on proper
file
|

|
Worksheet4.2: Issue Voucher
|
|
Instructions : verifying the
content of the issuing document and keep record on proper file
|
MINISTRY
OF HEALTH
ISSUE
VOUCHER
No………
TO
Requisition officer…….
|
S/N
|
Description of item
|
Unit
|
Quantity required
|
Quantity issued
|
Remarks
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date……………………….
ISSUING
OFFICER
Signature………..
Designation……..
REQUISITION OFFICER
Name…………...........................................
Signature………..
Designation……..
Session 5:
Premise Suitable for Storage of Medicines and
Medical Supplies
Total
Session Time: 120 minutes
Prerequisites
·
None
Learning
Tasks
By the end of this session students
are expected to be able to:
- Define
Storage of Medicines and Medical Supplies
- Explain
the Importance of Proper Storage of Medicines and Medical Supplies
- List Requirements of Premises for Storage of
Medicines and Medical Supplies
Resources
Needed:
·
Flip charts, marker pens, and
masking tape
·
Black/white board, chalk and whiteboard markers
·
LCD projector and computer
SESSION OVERVIEW
|
Step
|
Time
|
Activity/
Method
|
Content
|
|
1
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Introduction, Learning Tasks
|
|
2
|
20
minutes
|
Presentation
Brainstorming
|
Definition
of Storage of Medicines and
Medical Supply
|
|
3
|
40
minutes
|
Presentation
Small Group Discussion
|
Importance of Proper
Storage of Medicines and Medical Supplies
|
|
4
|
45
minutes
|
Presentation
Brainstorming
|
Requirements of Premises
for Storage of Medicines and Medical supplies
|
|
5
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Key
Points
|
|
6
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Evaluation
|
SESSION
CONTENTS
STEP1: Presentation
of Session Title and Learning Tasks (5minutes)
READ or ASK students to read the learning tasks and clarify
ASK
students if they have any questions
before continuing
STEP 2: Definition of Storage of Medicines and Medical
Supplies (20 minutes)
|
Activity: Brainstorming (5 minutes)
Ask students to brainstorm on the
following question:
- What
is storage of Medicines and Medical Supplies?
ALLOW few students to respond?
WRITE their responses on the flip
chart/ board
CLARIFY and SUMMARISE by using the content below
|
·
Storage of medicines and medical supplies
o
Is the safekeeping of medicines and Medical Supplies
to avoid spoilage and losses
STEP
3: Importance of Proper Storage of Medicines and
Medical Supplies
(40 minutes)
|
Activity: Small Group
Discussion ( 40 minutes)
DIVIDE students into small
manageable groups
ASK students to discuss on
the following question
- What
are the importance of proper storage of Medicines and Medical Supplies?
ALLOW students to discuss
for 20 minutes
ALLOW few groups to present
and the rest to add points not
mentioned
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE by
using the contents below
|
·
Proper storage of Medicines and
Medical Supplies are important in order to:
- Avoid
contamination or deterioration
- Avoid
disfiguration of labels
- Maintain
integrity of packaging and so guarantee quality and potency of Medicines
and Medical Supplies during shelf life
- Prevent
or reduce pilferage, theft or losses
- Prevent
infestation of pests and vermin
STEP 4: Requirements of premises for storage of Medicines and
Medical
Supplies (45 minutes)
|
Activity: Brainstorming (5 minutes)
Ask students to brainstorm on the
following question:
- What
are the requirements of premises for storage of Medicines and Medical
Supplies?
ALLOW few students to respond?
WRITE their responses on the flip
chart/ board
CLARIFY and SUMMARISE by using the content below
|
·
The following are requirements of
premises for Medicines and Medical Supplies:
o
Capacity/space: storage facilities
must have the capacity for both storage and handling
o
Cold storage: in larger facilities
it is more efficient to use cold rooms rather than numerous refrigerators or
freezers (which generate heat)
o
Secure storage: all Medical stores
should have a secure storage area for product that are likely to be stolen or
abused
o
Ventilation: the location designed
should ensure maximum air circulation to avoid concentration of fumes or gases
and to prevent condensation of moisture on products or walls
o
Roof: design a slanting roof to
allow water runoff
o
Ceiling: install a double ceiling to
provide insulation and ensure that supplies are kept cool
o
Walls and floor: the walls and
floors should be permanent and smooth for easy cleaning
o
Doors: plan doors wide enough to
allow for the free and easy movement of supplies and handling equipment
o
Lighting: plan the storeroom with as
much natural light (sunlight) in the day as possible to avoid the use of
florescent or incandescent bulb lighting
o
Windows: plan windows that are high
and wide to allow adequate ventilation
o
Cupboards: provide cupboards for the
storage of specific products that must be kept free from dust or light
o
First aid: keep well stocked first
aid kits to treat employees or visitors who are injured in your facility
o
Shelves: arrange shelves and racks
in lines with a passage way not less than 90 cm wide
STEP
5: Key Points (5 minutes)
·
Storage of Medicines and Medical
Supplies Is the safekeeping of medicines and Medical Supplies to avoid spoilage
and losses
·
Proper storage of Medicines and
Medical Supplies are important in order to maintain the their quality during
the whole period of their shelf life
·
Requirements of premises for
Medicines and Medical Supplies include: capacity/space, shelves, first aid kit,
cupboards, windows, lighting, doors, walls and floor, ceiling, roof,
ventilation secure storage and cold storage
STEP 6: Evaluation
(5 minutes)
- What is the storage of Medicines and Medical
Supplies
- What are the importance of proper storage of
Medicines and Medical Supplies?
- What are the requirements of the suitable premise
of Medicines and Medical Supplies
References
Management Science for Health and World Health Organization.
(1997). Managing Drug Supply, (2nd
ed.).West Hartford, Connecticut, USA: Kumarian Press
Shirima, L. L (1988): Basic Store-keeping and Warehouse
Management. General Publication United Republic of Tanzania, Public Procurement Act, 2004, Dar es
Salaam
Njau,
E. (2002). Pharmacology and Therapeutics (2nd ed.). Nairobi: African
Medical and
Research
Foundation
Total
Session Time: 120minutes
Prerequisites
·
None
Learning
Tasks
By the end of this session students
are expected to be able to:
·
Define
Zoning
·
Explain
Zoning of Stock Within the Store
·
Describe
Criteria for Establishing Zones Within a Store
·
Identify
Types of Stock Location Within a Zone
·
Describe
Stock Classification
·
Describe
the arrangement of Stocks in Zones
Resources
Needed
·
Flip charts, marker pens, and
masking tape
·
Black/white board, chalk and whiteboard
markers
·
LCD projector and computer
SESSION OVERVIEW
|
Step
|
Time
|
Activity/
Method
|
Content
|
|
1
|
5
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Introduction, Learning Task
|
|
2
|
5
minutes
|
Presentation
Brainstorming
|
Definition
of Zoning
|
|
3
|
20
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Zoning of Stock within the Store
|
|
4
|
10
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Criteria for Establishing Zones
within a Store
|
|
5
|
30
minutes
|
Presentation
Group
discussion
|
Types of Stock Location Within a Zone
|
|
6
|
30
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Stock
Classification
|
|
7
|
10
minutes
|
Presentation
Buzzing
|
Stock
Within a Zone
|
|
8
|
5
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Key
Points
|
|
9
|
5
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Evaluation
|
SESSION
CONTENTS
STEP1: Presentation of Session Title and Learning Tasks
(5minutes)
READ or ASK students to read the learning tasks and clarify
ASK
students if they have any questions
before continuing
STEP
2: Definition of zoning (5
minutes)
|
Activity: Brainstorming (3 minutes)
ASK students to brainstorm on the following question
ALLOW
few students to respond
WRITE
their answers on flip chart/ board
CLARIFY
and SUMMERIZE by using the content bellow
|
·
Definition
of zoning
- Is the
process of separating an area (building or room, a locked cupboard, a
refrigerator, a freezer, or a cold room), which should provide distinct
environmental conditions, a certain level of safety or the required level
of security.
STEP
3: Zoning of Stock within the Store (20
minutes)
·
Medicines and medical supplies must be stored in a zone/part of
the store with the correct combination of temperature and security as well as
the required level of safety and security. This initial zoning process is the
most basic way in which supplies can be arranged.
·
Follow to the extent possible, the product manufacturer’s storage
conditions
·
If no specific storage conditions are given, normal storage
conditions apply. Normal storage conditions for medicines have been defined as
storage in dry, well-ventilated premises at temperatures of 15ᴼC-25ᴼC
, or depending up climatic conditions, up to 30ᴼC (WHO 2003).
·
The 15ᴼC to 25ᴼC-30ᴼC temperature zone is
assumed to be air-conditioned and humidity controlled. In temperate climates
this temperature range can be achieved without air-conditioning, but humidity
control may still be necessary
·
Each storage zone should have at least one thermometer, and
temperature should be recorded daily at the hottest time of the day.
·
Storage at uncontrolled room temperature:
o
Many stocks can be safely stored at uncontrolled room temperature.
·
Cold storage:
- example of
drug products which usually require refrigeration:
§ insulin
§ Ergometrine
for injection
§ vaccines,
§ antitoxins
§ sera
and blood products
§ test kits/diagnostic tests
- These must
be stored in refrigerator or cold chains because their potency depends on
cold storage.
·
Secure storage:
o
This is necessary to protect drug products, which have higher risk
of theft, or to comply with national laws
o
Narcotics and other controlled drugs should be kept in a secure
room, a safe or steel cupboard/ cabinet to prevent access to unauthorized
persons
o
The keys to the secure store should be kept in a safe by a store
in-charge
o
Entry to the store must be controlled or restricted
·
Flammables e.g. alcohol/spirit, halothane, ether, must be stored
in special buildings or rooms. A separate building is the best because it
greatly reduces the risk of a fire spreading to the main store. The flammables
store must be well ventilated and fire proof; use water paints on the walls.
STEP 4:
Criteria for Establishing Zones within a Store (10minutes)
·
The selection of the storage zones
(as well as suitable storage equipment) is determined by various criteria:
- Required
storage temperature and humidity
- Size
of the product
- Volume
of batch
- Weight
of batch
- Requirement
for special storage equipment
- Dangers
posed by products
- Required
level of security
- Requirements
of national legislation
·
The required level of security for internationally
controlled drug products is determined by national legislation and regulations.
·
The level of security will also depend on the risk of
theft which may be high for internationally controlled drug products as well as
antibiotics, for example.
·
The number of items requiring specific storage
conditions as well as their average stock levels will determine the required
size each zone should have. For example a medical storage facility may require
only a small steel safe or a reinforced vault for storage of internationally
controlled drug products. Cold chain loads may require only a single refrigerator
or require a walk-in cold room.
·
Every product must be put away in
the zone with the storage conditions recommended by the manufacturer and
indicated on the packaging as well as according to the requirements by national
drug legislation.
·
While the storage in refrigerators
or locked rooms leaves no choice, many health care stock items can be stored on
floor pallets or on shelves. This choice is determined by the volume of batch
of each product.
·
Possible changes in the need for
different zones as well as the capacity of individual zones should be taken
into account from the very beginning. The zoning plan should be as flexible as
possible to allow future changes such as extension of the cold room with a
minimum of structural changes to the building.
STEP 5: Types of Stock Location within a
Zone (30 minutes)
|
Activity: Small Group
discussion(15 minutes)
DIVIDE
students into small manageable
groups
ASK
students to discuss on the
following question
- How are stock items arranged
in fixed, fluid and semi-fluid location systems?
- What are the advantages and
disadvantages for each of the systems above?
REFER
students to the recommended references
ALLOW
students to discuss for 10 minutes
ALLOW
few groups to present and the rest
to add point not mentioned
CLARIFY
and SUMMERIZE by using the content below
|
·
Types of location within zones:
- Fixed location
- Fluid location
- Semi-fluid location
·
Fixed location:
- In fixed location system, each stock item is
allocated to specific shelves, pallet racking or an area of floor. For
this system to work well, the store has to be large enough to accommodate
the maximum possible level of stock for every item, including safety
stock. As stock is used up, the storage location is emptied and left
vacant until a new shipment of the item is received.
- Advantage:
§ Simplest to
manage/ stock administration is relatively easy because each stock item can
always be found in the same place.
§ Fixed
location systems are inflexible. If there is a change in the quantity ordered
or a change in packaging, the assigned location may become too large or too
small.
§ If a new
item is ordered, there may be no place to store it.
§ Theft may
increase because all store staff are familiar with the locations of valuable
items.
§ Storage
space may be wasted, because at times it is largely empty
·
Fluid location
- The store is divided into many designated
locations. Each location is assigned a code. Individual items are stored
wherever space is available at the time of delivery.
- Administration for a fluid location system works
as follows:
§ The
procurement unit provides information on the type, volume, and weight of goods
arriving.
§ The store
keeper asses which locations will be empty when the new stock arrives and
assigns an appropriate location. These data are recorded in the stock control
system.
§ If
insufficient space is available, other stock items may be moved to create more
space
§ The stock
control location records are updated.
- Fluid location systems require a classification
system that allocates a unique identifier code to each stock item and to
each location. Also the stock record for each batch of each item must
always indicate the physical location of the item in the store.
- In a fluid location system, different batches of
a particular item may be stored in several different places (give an
example).
- This systems benefit immensely from the use of a
computerized bin location and storage system, which improves productivity
and optimizes storage capacity. Such systems identify locations of items
and the best locations for storing an incoming consignment within the
storage areas.
- Advantages:
§ It uses
available space efficiently because none of the places has to be reserved for
any specific item.
§ Batches of
items never have to be moved or relocated to maintain a certain order.
§ It requires
sophisticated stock administration due to the difficulty of keeping track of
the storage places of all batches.
§ Different
batches of the same item may be stored in different places which makes strict
stock rotation and FEFO/FIFO management difficult.
§ In case of
errors, stock may be lost
·
Semi-fluid location:
- A Semi-fluid location system is a combination of
the fixed and fluid systems.
- Each item is assigned a fixed space for picking
stock. When an order is prepared, the order-picking staff members know
where to find each item.
- The remainder of the store is filled on the fluid
location principle. When the picking stock runs low, the fixed locations
are restocked using items from the fluid locations.
- Advantages:
§ Picking stock
is always kept in the same place
§ Picking
stock is stored at a convenient height, eliminating the need for mechanical
handling during order picking in stores that issue in relatively small
quantities.
§ If demand
increases for a particular item, the picking stock can be replenished more
frequently
§ As new
products are introduced, picking bays may be subdivided to provide sufficient
space.
§ It is not as space-efficient as a fluid
location system.
§ Risk exists
(though less, unlike in a fixed location) that changing requirements will
disrupt the system.
STEP 5: Stock
Classification (30minutes)
·
Items should be clearly organized within each zone of
the store. Such organization makes it much easier for store personnel to
control stock, take periodic stock inventory and pick orders.
·
Some common systems for arranging medicines include:
o
Therapeutic / pharmacological category
o
Alphabetical order by generic name
o
Dosage form
o
Random bin
o
Frequency of use
o
System level
o
Commodity code
o
Combination
·
Therapeutic category:
- May be an effective way of organizing medicines
in smaller stores and in the dispensaries of small clinical facilities
where the store-keeper is the dispenser and also very knowledgeable about
pharmacology. It is not an advantage in large stores.
- Disadvantage:
§ Applicable
only to drug products
§ Ambiguous
·
Clinical indication:
- Similar to therapeutic category and may be
convenient in small warehouses.
- All hypertensives are together as are all
antidiabetics or other drugs with a common clinical indication.
- One problem is that many drugs have multiple
clinical indications.
- A clinical indication system therefore requires a
level of professional knowledge that stores staff are unlikely to have.
- If staff do acquire this knowledge, theft may
become a problem
·
Alphabetical order by generic name:
- Is also
attractive in peripheral store that keep a small number of items, but
often seen in both large and small facilities.
- When using this system, the labelling must be
changed when the National Essential Medicine List is revised or updated
- Advantages:
§ Requires no
knowledge about nature and use of items
§ Applicable
to any item
§ Mixes very
different items
§ Does not
consider appropriate zones (temperature, safety, security etc.)
·
Dosage form:
- Medicines
come in different forms, such as tablets, syrups, injectable, and external
use products such as ointments
and creams. In this system, medicines are categorized according to their
dosage form.
- Within the area for each form, a fixed, fluid, or
semi-fluid system is used to store items. Any of the other methods of
categorizing can be used to organize the items more precisely.
- Advantage:
§
The forms are easy to recognize when
receiving stock items-does not require much skill
§
Allows optimal use of space
§
Applicable only to drug products
·
Random bin
- Identifies
a specific storage space or cell with a code that corresponds to its
aisle, shelf, and position on the shelf.
- For
example, a shelving unit can be divided vertically and horizontally into
cells, each cell with a specific location code. A unit of shelving might
be labeled “B”, its bays “B1” and “B2” and
its shelves “A,” “B” and “C”. A specific
cell would be identified, for example as B1-B, this cell is called a bin.
- This
method can combine the methods described above. For example, items are
placed alphabetically within therapeutic classification. Generic names are
used throughout. If there is more than one brand of the same generic drug
preparation, all are stored in the bin for that type.
- This
system requires computer automation.
·
System level:
- Items
for different levels of the health care system are kept together. This
works well in stores at a higher level when storage of kits is required.
- Advantage
§
Reduce time required for put-away
and order picking
§
Level of use need to be determined
for each item
§
More storage space is required
because many commonly used items appear at more than one level.
§
Distribution on a FIFO/FEFO basis
becomes more difficult to achieve
§
One of the other methods of organization is needed within each level
of use to avoid chaos
·
Frequency of use
- Frequently used products that move quickly or
often through the store should be placed in the front of the room or
closest to the staging area. This system should be used in combination
with another system.
·
Commodity coding
- Each
item has its own article and location code. This system has the greatest
flexibility, but it is also the most abstract.
- It
is based on a unique/specific article code combined with a unique/
specific location code
- Store
keeping staff do not need any technical knowledge of the products to
manage this system because the codes contain the information needed for
storing products properly, such as temperature requirements, level of
security, and flammability or clinical indication, level of use or any
other relevant data.
- Changes
in the national medicine list can easily be introduced by assigning unique
article codes to new products.
- This system works well in computerized
inventory control systems.
- The
location code is totally independent of the article code and is similar to
the random bin principle.
- Codes
can be designed to incorporate any number of characteristics including
§
Correct storage temperature for the
product
§
Correct security level for the
product
§
Whether the product is flammable
§
The building where the product is
located
§
Pack size
§
Pharmaceutical form
§
Same logical order inherent in the
coding
§
No pharmaceutical knowledge needed
§
Groups often correspond to required
storage conditions
§
Applicable to all items
§
Increases security, but still allows
items to be identified by those staff who have access to the coding key.
§
Codes must be known or looked up
§
Order may not be entirely consistent
STEP 6: Arrangement of Stock within
a Zone (10minutes)
·
Organizing
stock systematically saves time when ordering or locating items and prevents
stock from being lost.
·
The
systems most often used in health facilities are organization by therapeutic
category, clinical indication or dosage form with products arranged
alphabetically within those categories.
·
Liquids
for internal use must be kept separate from those for external use
|
Activity: buzzing (5 minutes)
ASK
students to pair up and buzz for 5
minutes on the following question
- What is the importance of
arranging liquids for external use and internal use in different zones?
ALLOW
few pairs to respond
WRITE
responses on the flip chart/ board
CRALIFY
and SUMMERIZE by using the content bellow
|
STEP 7: Key Points (5 minutes)
·
Zoning/setting up of stock within the
store: Medicines and medical supplies must be located in a part of the store
with the correct combination of temperature and security. This initial zoning
process is the most basic way in which supplies can be arranged.
·
Criteria for establishing zones within
a store include required storage temperature and humidity, size of the product,
volume of batch, weight of batch, requirement for special storage equipment,
dangers posed by products, required level of security and requirements of
national legislation.
·
Types of stock location within a
zone are fixed, fluid and semi-fluid locations.
·
Stocks may be classified or
organized by the following methods; therapeutic / pharmacological category, alphabetical
order by generic name, dosage form, random bin, frequency of use, system level,
commodity code or a combination of other methods.
·
Arranging stocks systematically
saves time when ordering or locating items and prevents stock from being lost.
STEP 8: Evaluation (5minutes)
·
Define
zoning?
·
What
are the criteria of establishing zones within the store?
·
What
are the stock locations within a zone?
References:
Management Science for Health and World Health Organization.
(2012). managing access to medicines and
health technology, (3rd ed.). Kumarian Press
Management Science for Health and World Health
Organization. (1997). Managing Drug
Supply, (2nd ed.).West Hartford, Connecticut, USA:Kumarian Press
World Health Organization (WHO), Regional Office for Africa
Brazzaville (2004), Management of Drugs
at Health Centre Level Training Manual.
Shirima, L. L (1988): Basic Store-keeping and Warehouse Management.
General Publication
Jessop, D and Morrison (1994) Storage and Supply of Materials, (6th
ed.), Prentice Hall
Laurie L, Editor, (2003) Guidelines
for the Storage of Essential Medicines and Other Health Commodities. John Snow,
Inc./deliver in collaboration with the World Health Organization
Guire G. Mc (2011), handbook
of humanitarian health care logistics: designing the supply
network
and managing the flows of information and health care goods in
humanitarian assistance during
complex political emergencies
(2nd ed.). Retrieved
fromwww.humanitarianhealthcarelogistics.com
Total
Session Time: 120 minutes
Prerequisites
·
None
Learning Tasks
By the end of this session students are expected to be able to:
·
Define Quality of Medicines and
Medical Supplies
·
List Factors Affecting Quality of
Stored Medicines and Medical Supplies
·
Explain the Consequences of Poor
Storage of Medicines and Medical Supplies
·
Describe Ways to Avoid the Effects
of Medicines and Medical Supplies Deterioration.
·
Identify Signs of Deteriorated
Medicines
Resources
Needed:
·
Flip charts, marker pens, and
masking tape
·
Black/white board, chalk and whiteboard
markers
·
LCD projector and computer
SESSION OVERVIEW
|
Step
|
Time
|
Activity/
Method
|
Content
|
|
1
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Introduction, Learning Tasks
|
|
2
|
10
minutes
|
Presentation
Brainstorming
|
Definition
of Medicines and Medical Supplies
|
|
3
|
15
minutes
|
Presentation
Buzzing
|
Factors
Affecting Quality of Stored Medicines and Medical Supplies
|
|
4
|
30
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Consequences of Poor Storage of
Medicines and Medical Supplies
|
|
5
|
35
minutes
|
Presentation
Small
group discussion
|
Ways to Avoid the Effects of
Medicines and Medical Supplies Deterioration.
|
|
6
|
15
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Identification of Signs of Deteriorated Medicines
|
|
7
|
5
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Key
Points
|
|
8
|
5
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Evaluation
|
SESSION
CONTENTS
STEP1:
Introduction, Learning Tasks (5 minutes)
READ or ASK students to read the learning tasks and clarify
ASK
students if they have any questions
before continuing
STEP 2: Definition
of Quality of Medicines and Medical Supplies
(10
minutes)
|
Activity: Brainstorming (5 minutes)
ASK students to brainstorm on the
following question:
- What
is quality of medicines and medical supplies?
ALLOW few pairs to respond and let
other pairs to add on points not mentioned
WRITE their response on the flip
chart/board
`
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE by using the content below
|
·
Quality of medicines and medical
supplies
- Quality
of medicines and medical supplies can be defined in terms of suitability
for the intended use. Thus,
several aspects are of importance are efficacy and safety of the product
conformity with specifications in terms of identity strength, purity and
other characteristics as specified in pharmacopoeia or pharmaceutical
regulations.
STEP 3 Factors Affecting Quality of Stored Medicines
and Medical Supplies
(15 minutes)
|
Activity: Buzzing (5 minutes)
ASK students to pair up and buzz on
the following question for 5 minutes
- What
are factors affecting quality of stored medicines and medical supplies?
ALLOW few pairs to respond and let
other pairs to add on points not mentioned
WRITE their response on the flip
chart/board
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE by using the content below
|
The following are factors which
affect the quality of stored medicines and medical supplies
·
Heat
·
Temperature
·
Moisture
·
Light
·
Microbial
contamination
·
Air
·
Humidity
·
Cold
·
Rats and
mice
STEP 4: Consequences of Poor Storage of Medicines and Medical Supplies
(30
minutes)
·
Heat
o
Heat leads
to chemical decomposition, protein denaturation
·
Temperature
o
Temperature
may cause some compound to melts e.g. ointment and become useless.
·
Moisture
o
Moisture
can cause tablet to crumble
·
Light
o
Strong
light will damage many medicine
·
Microbial
contamination
o
Microbial
contamination may contaminate with medicines ingredients and cause infection
·
Air
o
The
chemicals in drugs can slowly react with the oxygen in the air
·
Humidity
o
Too high
humidity may cause growth of fungus and mould in the stored medicines
·
Cold
o
In very
cold condition liquid medicine may freeze. Some vaccines, if they have been
frozen should not be used.
·
Rats and
mice
o
Can chew
through containers made of most materials around the content to become
contamination
STEP 5: Describe Ways to Avoid the Effects of Medicines
and Medical Supplies Deterioration (35 minutes)
|
Activity: Small Group Discussion (
15 minutes)
DIVIDE students into small manageable groups
ASK
students to discuss on the
following question
·
What are the
ways to avoid the effect of medicines and medical supplies deterioration?
ALLOW students to discuss for 15 minutes
ALLOW few groups to present and the rest to add points not mentioned
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE
by using the contents below
|
·
Temperature
o
Temperature effect is avoided by
storage in cold conditions, refrigerator, room temperature and other
temperature depending on a specific type of drug.
o
In the storage room one must
§
Maintain a refrigerator temperature
2-8 C using thermometer
§
Keep freezers and refrigerators in
shady, ventilated area
§
Record temperature in room and
refrigerator three times a day
§
Compare the recorded temperature
with the recommended temperature of their medication
§
Minimize frequency and duration of
opening the refrigerator
§
Keep the refrigerator well organized
§
Use refrigerator exclusively for
medical product, not for food
·
Humidity
o
In humid climate, dehumidifiers are
used for preventing moisture damage
o
If there is no dehumidifiers use
ventilating fans or opens windows
·
Light
o
Keep liquids in tinted glass
o
Keep light sensitive items in their
originally package
o
Protect from sun
·
Air
o
Well-fitting lids on containers
o
When you open containers keep it
open for the shortest possible time
o
Replace their lids securely and
promptly
·
Rats and mice
o
Make your store as
“rat-proof”,
o
Use fine wire mesh in wall cracks
and windows
o
Stores good in pallets or shelves
not on the floor
o
Use rats trap or poison to kill rats
·
Moisture
o
Moisture effect is avoided by
ensuring aeration in the store, ensure the store is dry, some drugs contain
sachets, ensuring drugs are retained in their original container, drying of
hands when handling drugs, the use of pellets
·
Heat
o
Store should be built in the shade
or nearby trees
o
Supplies should be kept out of
direct sunlight
STEP 6: Identification of Signs of
Deteriorated Medicines (15minutes)
·
Some damage can easily identified by looking at the
damaged drugs or containers. A close examination of some damaged medicines can
results the following
Medicines
Sign of damage
1 –
Compressed tablets swollen,
crumpled and damp
2 –
Ointments
melted
3 –
Adrenaline injection changes to
brown colour
4 – Any
medicine
moulds or fungus growing
5 –
Medicine containers holes or
marks
6 –
Tablets
broken
STEP 7: Key Points (5 minutes)
·
Quality
of medicines and medical supplies refers to suitability for the intended use.
·
Factors
which affect the quality of stored medicines and medical supplies include heat,
temperature, humidity, light, air, etc.
·
Medicines and medical supplies that are deteriorated
can easily identified by looking at the damaged medicines or packaging
materials
STEP 8: Evaluation (5minutes)
·
What are special storage conditions applicable
to medicines and medical supplies?
·
What are
the factors that affect quality of stored medicines and medical supplies?
·
What are the
ways to avoid the effect of poor medicines storage?
·
What
are the consequences of poor storage of medicines and medical supplies?
·
What
are identification signs of deteriorated medicines
References
Ministry of Health and Social
Welfare (MOHSW) ( 1997 ). Wizara ya Afya
na Ustawi wa Jamii cha muongozo
wa utoaji sahihi na dawa . Dar es salaam : Tz Ministry of Health and Social
Welfare
Guidelines on the storage of
essential drug in eastern and southern Africa (1991) by WHO with the
cooperation of the pharmaceutical industry through the International Federation
of Pharmaceutical Association IFPMA
Management Science for Health and World Health Organization.
(1997). Managing Drug Supply, (2nd
ed.).West Hartford, Connecticut, USA: Kumarian Press
Session 8: Ordering of Medicines and
Medical Supplies
Total
Session Time: 120 minutes
Prerequisites
·
None
Learning
Tasks
By the end of this session students
are expected to be able to:
·
Define Ordering of Medicines and
Medical Supplies
·
Explain the Procedure for Ordering
Medicines and Medical Supplies
·
Identify Stock Records Required for
Ordering Medicines
·
Practice Filling and Completing
Order Forms Used in the Facility.
Resources
Needed:
·
Flip charts, marker pens, and
masking tape
·
Black/white board, chalk and whiteboard
markers
·
Handout 8.1. Ordering of Medicines
and Medical Supplies
·
Worksheet
8.1.Sample of report and Request Form
·
Worksheet
8.2: Answers for Small Group Discussion
·
LCD
projector and computer
SESSION OVERVIEW
|
Step
|
Time
|
Activity/
Method
|
Content
|
|
1
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Introduction, Learning Task
|
|
2
|
10
minutes
|
Presentation
Buzzing
|
Definition of Ordering of
Medicines and Medical Supplies
|
|
3
|
25
minutes
|
Presentation
Buzzing
|
Procedures for Ordering Medicines
and Medical Supplies
|
|
4
|
10
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Stock Records Required for
Ordering Medicines
|
|
5
|
60
minutes
|
Presentation
Small
Group Discussion
|
Filling and Completing Order Forms
Used in the Facility.
|
|
6
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Key
Points
|
|
7
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Evaluation
|
SESSION
CONTENT
STEP1:
Introduction, Learning Tasks (5 minutes)
READ or ASK students to read the learning tasks and clarify
ASK
students if they have any questions
before continuing
STEP
2: Definition of Ordering of Medicines
and Medical Supplies
(10 Minutes)
|
Activity: Buzzing (5 minutes)
Ask students to pair up and buzz on
the following question for 2 minutes:
- What
is ordering of medicines and medical supplies?
ALLOW few students to respond
WRITE their responses on the flip
chart/ board
CLARIFY and SUMMARISE by using the content below
|
·
Ordering
of medicine and medical supplies
- Is a process of placing a request to a supplier
to get needed stock.
·
Things to
consider while planning to order new stock are
o
What to
order
o
When to
order
o
How much
to order
STEP
3: Procedures for Ordering Medicines and Medical Supplies
(25 Minutes)
|
Activity: Buzzing (5 minutes)
Ask students to pair up and buzz on the
following question for 2 minutes:
- What
are the procedures for ordering medicines and medical supplies?
ALLOW few students to respond
WRITE their responses on the flip
chart/ board
CLARIFY and SUMMARISE by using the content below
|
·
The ordering process starts with
pharmaceutical personnel and medical officers in charge of the facility filling
out a monthly/quarterly R&R (Report and Request) form
·
The completed form is sent to the
District Medical Officer for approval and with the assistance of District
Pharmacist these forms are compiled together and then sent to MSD
·
MSD reviews the order and delivers
the required items with sales invoice to the District
·
The District Medical
Officer/Pharmacist receives the medicines and related supplies for the district
and distributes them to the facilities according to the order
·
The ordering of medicines is
normally done quarterly or monthly
·
Excessive stock is wasteful and should be
avoided and on the other hand ordering too little will result in shortages

 Refer students to Handout8. 1.
Ordering of Medicines and Medical Supplies for further reading
Refer students to Handout8. 1.
Ordering of Medicines and Medical Supplies for further reading
STEP
4: Stock Records Required for Ordering Medicines (10 minutes)
·
Stock record and Bin Cards
- Very
important tools used to control the stock movement of items in the store
- Each
item has its own bin card and should be displayed on the shelf where the
product is located
- It
is necessary to do actual counts of stock on hand to check the stock
balance on regular basis (monthly)
- The
inventory taking should certify that the recorded transactions are
accurate
·
Store ledger
- Usually
kept in the office of the store in-charge
- Contains
information similar to bin cards
- Each
item has its own page and in additional to a part where one has to fill in
the amount of medicine expired, broken or lost and the remarks.
·
Report and Request Form (R&R)
- A
form used for reporting the movement of medicines and commodities through
the facility, and also requesting quantities of stock needed to replenish
supplies
·
Dispensing register
- This
is the book which used to record medicine dispensed
STEP
5: Filling and Completing Order Forms Used in the Facility. (60 minutes)
|
Activity: Small Group Discussion (
30 minutes)
DIVIDE students into small manageable groups
ASK
students to discuss on the following
question
Today is 1st of January
2008 and it is time for Jamhuri hospital of Kisarawe district to complete R
& R for HIV test kits. The following information was obtained for the
past three months usage data. The facility code is 00475534
Group work
·
The
store ledger shows that by 30th September 2008 the physical
inventory for SD Bioline was 24 kits, Determine 1 kit, Unigold 3 kits
·
For the
period of October 1st to December 31st 2008 the
facility received 16 kits, of SD Bioline, 1 kit of Determine and 0 kit of
Unigold
·
During
the same period daily usage records from VCT/PITC indicates that 355 tests of
SD Bioline, 21 of Determine and 4 of Unigold were used whereas from PMTCT 250
tests of SD Bioline, 21 of Determine and 3 of Unigold were used for PMTCT
purposes
·
For the
same period the usage record from lab indicated that 250 tests of SD Bioline,
10 of Determine and 5 of Unigold
·
A nearby
health centre called Mwendapole Health centre borrowed 100 tests (given: 1
kit of SD Bioline has 25 tests, Unigold as 25 tests, Determine 100 tests)
ALLOW students to discuss for 15 minutes
ALLOW few groups to present and the rest to add points not mentioned
 REFER students to worksheet 8.2 for answers. REFER students to worksheet 8.2 for answers.
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE
by using the contents below
|
STEP 6: Key Points (5 minutes)
·
Effective ordering ensure access to
constant supply of quality medicines and medical supply
·
Proper documentation of medicines is
essential to ensure good supply of medicines
·
Medicines should be ordered by
generic names
·
Order quantity shall be based on
estimate of the actual needs
STEP 7: Evaluation (5 minutes)
·
Define ordering of medicines and
medical supplies?
·
Explain the procedure for ordering
medicines and medical supplies?
·
Identify stock records required for
ordering medicines?
References
Ministry of Health and Social
Welfare (MOHSW) (1997). Wizara ya
afya na ustawi wa jamii cha muongozo
wa utoaji sahihi na dawa. Dar es Salaam: Tz Ministry of Health and Social
Welfare
Guidelines on the storage of
essential drug in eastern and southern Africa (1991) by WHO with the
cooperation of the pharmaceutical industry through the International Federation
of Pharmaceutical Association IFPMA
Management Science for Health and World Health Organization.
(1997). Managing Drug Supply, (2nd
ed.).West Hartford, Connecticut, USA: Kumarian Press

|
Handout 8.1: Ordering of Medicines and Medical Supplies
|
|
|
|
Ordering by Dispensaries and health
centers under the ILS, dispensaries and health centers will submit orders
quarterly (every 3 months) to the DMO for the supplies to meet the needs of
their clients. The facility in- charge determines the quantities of supplies
they need and ensures that the quantities they order can be paid for and
respond to the level of services that are provided by qualified health care
workers.
The principles described below guide
aspects of the ordering process. Detailed instructions can be found in the Job
Aid:
Completing Form 2A: Dispensary or
Health Center Report & Request for priority medicines and related supplies
and equipment.
Form 2B: Hospital Report &
Request for Priority Medicines and Related Supplies and Equipment.
Form 2C: Blank Report & Request
for Additional Medicines and Related Supplies and Equipment at the Dispensary
or Health Center, or Hospital.
1. Ordering is done through Form 2A:
Dispensary and health center Report & Request for priority medicines and
related medical supplies and equipment (R&R) and form 2C:
Blank Report & Request for additional
medicines and related supplies and equipment. The Dispensary or health Center
storekeeper determines the quantity of each product to order using Form 2A:
Dispensary and health center Report
& Request for Priority and related medical supplies and equipment. The
names of the products, MSD code, unit of issue, and price for each item are
pre-printed on the R&R form.
The storekeeper or health facility
in-charge is required to order all priority supplies each quarter, unless the
product is already at or above its maximum stock level. (See the explanation
below on maximum stock levels.) That is
because priority supplies are the most important supplies to keep in
stock.
If the facility does not ever use a
specific product (e.g., some facilities may not ever issue intrauterine devices
(IUDs) due to a lack of trained staff), it should not be ordered.
2.
Calculating the Quantity Requested To determine how much to request,
Form 2A: R&R includes a formula for ordering. That formula is based on logistics data,
which is about quantities of supplies (as opposed to numbers about people or
services, often called demographic or service statistics data). The logistics data needed to make orders are
collected on Stores Ledgers (or MTUHA book 4 if it is being used) and are taken
from the previous
The logistics data that will be
taken from these forms and transferred to the R&R include:
Opening Balance The opening balance
is taken from the ending balance for the facility from the previous
quarter‘s Form 2: R&R (or the closing balance for the MTUHA book 4 for
the facility ordering the first time.)
Quantity received this reporting
period the quantity received this period is taken from Stores Ledger and
includes all receipts of supplies received by the dispensary or health center
from the district.
Lost/Adjusted Losses and adjustments
are taken from Stores Ledger and would reflect the total net change in stock
for the quarter due to expiration, damage, transfers (issue on loan/receipt on
loan), clerical error or other reasons.
For example, if there were a loss of 50 and a transfer in of 100, the
total adjustment recorded on Form 2: R&R would be +50 (a positive sign for
quantity gained and a negative sign for quantities lost).
Closing -Balance The closing balance
for the facility tells how much of each product the facility currently has
available for use. The ending balance
should always be taken from a physical inventory conducted at the end of the
month. See Section VIII-C for
information on conducting a physical inventory.
Estimated Quarterly Consumption The
estimated quarterly consumed quantity is the estimated total quantity of a
product put in the hands of a client during the quarter. While it would be possible to collect the
actual data by reviewing all registers and client cards for the entire quarter,
that method would be extremely time-consuming.
Consequently, a simpler formula for estimating consumption for the ILS
has been developed. That formula
is:
Opening balance + Received This
Period ± Lost/ Adjusted Closing Balance
=
Estimated Consumption
The estimated consumption has to be
adjusted for products for which there has been a stock out during the reporting
period. Stock outs are expected to be rare if products are appropriately
ordered to the maximum stock level.
Refer to Job Aid: Handling Stock
outs when Completing Form 2 A-C R & R
If there are frequent stock-outs,
then try to find out why the stock-outs are occurring. Are they due to
increased dispensing? Are they due to loss, expiry or damage? Were the order
quantities for those supplies reduced due to insufficient funds? If a
particular cause can be identified for the stock-outs, try to address and
resolve the issue.
Quantity Needed: Based on a System
of Maximum-Minimum Inventory control method of determining stock levels
The maximum stock level for priority
medicines and medical supplies in the ILS is fixed at 7 months of stock. The use of 7 months of supply as the maximum
is based on the fact health facilities will order all priority supplies every 3
months. A 7 month maximum will provide a
facility sufficient stock of each priority supply to use during the quarter (3
months of supply), two months of supply while orders are being processed and
shipped, and two months of buffer stock in the event that the need for any
supply increases. Therefore, a 7 month
maximum should help ensure that no priority supply will be stocked out at any
time.

|
Worksheet 8. 1: Sample of report
and Request Form
|
|
Instructions
:Filling of R and R form
|

|
|

|
Worksheet 8. 2: Answers for Small
Group Discussion
|
|
|
Instructions:
Student shall make comparison of their answers with the answers provide
below.
|
Session 9: Receiving Medicines and Medical
Supplies
Total
Session Time: 120 minutes
Prerequisites
·
None
Learning
Tasks
By the end of this session students
are expected to be able to:
·
Define Receiving of Medicines and
Medical Supplies
·
Explain the Procedures for Receiving
Medicines and Medical Supplies
·
Identify Stock Records Required for
Receiving of Medicines and Medical Supplies
·
Practice Filling and Completing
Order Forms Used in the Facility
Resources
Needed:
·
Flip charts, marker pens, and
masking tape
·
Black/white board, chalk and whiteboard markers
·
LCD projector and computer
·
Handout 9.1: receiving of medicines and medical supplies
·
Worksheet 9.1: Sample of Good
Received Note
SESSION OVERVIEW
|
Step
|
Time
|
Activity/
Method
|
Content
|
|
1
|
5
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Introduction, Learning Task
|
|
2
|
10
minutes
|
Presentation
Brainstorming
|
Definition of Receiving of
Medicines and Medical Supplies
|
|
3
|
25
minutes
|
Presentation/
Buzzing
|
Procedures for Receiving Medicines
and Medical Supplies
|
|
4
|
10
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Stock Records Required for
Receiving Medicines
|
|
5
|
60
minutes
|
Presentation
Small
Group Discussion
|
Filling and Completing Receiving
Forms Used in the Facility.
|
|
6
|
5
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Key
Points
|
|
7
|
5
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Evaluation
|
SESSION
CONTENT
STEP1:
Introduction, Learning Tasks (5 minutes)
READ or ASK students to read the learning tasks and clarify
ASK
students if they have any questions
before continuing
STEP 2: Definition of Receiving of Medicines
and Medical Supplies
(10 Minutes)
|
Activity: Brainstorming (5 minutes)
ASK students to brainstorm on the
following question:
- What
is receiving of medicines and medical supplies?
ALLOW few pairs to respond and let
other pairs to add on points not mentioned
WRITE their response on the flip
chart/board
`
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE by using the content below
|
·
Receiving of medicine and medical supplies
- Is a process of receipt medicine and medical
supplies from selected qualified vender.
·
When
receiving medicines and medical supplies the following information should
recorded in the store ledger and bin card:
- date of received
medicines and medical supplies
- the name of the supplier
- quantity of medicines and medical supplies
received Unit price
STEP 3: Procedures for Receiving Medicines and Medical
Supplies
(25 Minutes)
|
Activity: Buzzing (5 minutes)
Ask students to pair up and buzz on
the following question for 2 minutes:
- What
are the procedures for receiving medicines and medical supplies?
ALLOW few students to respond
WRITE their responses on the flip
chart/ board
CLARIFY and SUMMARISE by using the content below
|
·
Within a facility, items should be
received by the pharmaceutical personnel and approved by Hospital/health
facility Therapeutic Committee (HTC)
·
Products received should also be
entered into stock cards/bin cards and the store ledger
·
Delivery note and sales invoice should be used
for comparing with the actual receipts
·
If any discrepancy is observed,
verification claim forms must be filled out and sent to MSD or other suppliers
·
A room for keeping pharmaceutical
products should meet all the specification required
·
, Keep medicines and medical
supplies in their appropriate storage conditions e.g. refrigerated medicines to be kept in the refrigerator

 Refer students to Handout 9.1
Receiving of Medicines and Medical Supplies for further reading
Refer students to Handout 9.1
Receiving of Medicines and Medical Supplies for further reading
STEP 4: Stock Records Required for Receiving Medicines (10
minutes)
Stock records required for receiving
medicines in a store are:
o
Verification and claim form
o
Goods Received Note ( GRN )
 REFER students to worksheet 9.1 for further reading.
REFER students to worksheet 9.1 for further reading.
STEP
5: Filling and Completing Receiving Forms Used in the Facility.
(60 minutes)
|
Activity: Small Group Discussion (
30 minutes)
DIVIDE students into small manageable groups
ASK
students to discuss on the
following question
INSTRUCT
students to fill in verification and claims form for the exercises 1 and 2
below.
Exercise 1:
100 tins of Lamivudine 150mg, ordered, listed on the MSD
sales invoice but not received.
Use the name of any facility, supplier, transporter and
driver that you know. Assume the
ordered quantity was 500 tins in the form number 034.
Exercise 2:
3 tins of Abacavir 300mg tablets, received on 30th June
2009, with less than 3 months shelf life remaining. Expiry date 30th
September 2009
ALLOW students to discuss for 30 minutes
ALLOW few groups to present and the rest to add points not mentioned
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE
by using the contents below
|
STEP 6: Key Points (5 minutes)
·
Receiving of medicine and medical supplies is a process of receipt medicine and
medical supplies from selected qualified vender.
·
Within a facility, items should be
received by the pharmaceutical personnel and approved by Hospital/health
facility Therapeutic Committee (HTC)
o
Stock records required for
receiving medicines include verification
and claim forms and goods received note ( GRN )
STEP 7: Evaluation (5 minutes)
·
What is receiving of medicines and
medical supplies?
·
What are
the procedures for receiving medicines and medical supplies?
·
What are stock records required for
receiving of medicines and medical supplies?
.
References
Ministry of Health and Social
Welfare (MOHSW) (1997). Wizara ya
afya na ustawi wa jamii cha muongozo wa utoaji sahihi
na dawa . Dar es Salaam: Tz Ministry of Health and Social Welfare
Guidelines on the storage of
essential drug in eastern and southern Africa (1991) by WHO with the
cooperation of the pharmaceutical industry through the International Federation
of Pharmaceutical Association IFPMA
Management Science for Health and World Health Organization.
(1997). Managing Drug Supply, (2nd
e.d.).West Hartford, Connecticut, USA: Kumarian Press

|
Handout 9.1: receiving of Medicines and Medical Supplies
|
A. Dispensary and Health Center Level
It
is the responsibility of the DMO to ensure that the pre-packaged supplies
received
Quarterly
from MSD are delivered to each facility in time. The process by which the supplies are
received at the facility.
1)
Facility waits for supplies from district
until week 3 of month 3 of the quarter.
According
to the delivery schedule in Section V-Ordering, supplies should be delivered
from the DMO to health centers and dispensaries by the end of the third week of
the third month of the quarter. (For
example, if the quarter is Feb/Mar/Apr, the expectation is that the order will
be received within the third week of April.)
2)
Is delivery on time? The Facility-In-charge should check to see if the truck
coming from the district is on time.
2a)
Shipment at district?—If the supplies do not arrive on time, the facility
in-charge should contact the district to determine if MSD has delivered the
facility‘s order to the district.
2b)
Wait until shipment at district.—If the facility‘s order is not at
the district, the facility should wait until it has arrived.
2c)
Shipment at the district but not delivered to the facility on time? -Facility
in charge should follow up with the DMO. Determine if the District can arrange
to deliver the shipment in good time, otherwise, arrange pick up.
3)
Facility receives shipment, noting date on the district generated transaction
record. The facility should maintain records of the GRN or the district
generated transaction record to enable monitoring of deliveries. The district
should deliver these cartons, intact, to the facilities. At the facility, the facility in-charge will
count the number of cartons and sign for that receipt. The contents of the
cartons will not be known until they are opened later.
4)
Open cartons with a Village Health Committee (VHC) member and two other
Witnesses
present As soon as possible after the shipment arrives at the facility the
in-charge should notify the VHC and arrange for a member(s) to be present for
the opening of the carton. It is necessary that this step be completed
immediately after the receipt of the sealed cartons. If no member of the
Village Health Committee is available, the facility in charge should contact
the village government which would name a person to be a witness. Both the facility in charge and the village
health committee member and witnesses should compare what is delivered with
what is on Form 4: MSD Sales Invoice In
case of any discrepancies, unacceptable shelf life, or damage, the facility
in-charge should fill out and sign Form7.Verification
and Claims Form in
triplicate (packed inside one of the cartons) to be signed by all three
witnesses. A copy of Form 7 is retained at the facility, a copy is sent to the
DMO and the original sent to MSD. To MSD.
The
box will also contain Form 5: Customer
Statement of Account which should be given to the Facility In
charge. The statement of account will be
used to determine the amount of the central allocation that can be spent for
the next order.
5)
Record receipt in Stores Ledger.
All acceptable supplies should be recorded the Stores Ledger/MTUHA Book 4.
Unacceptable supplies should be quarantined (separated) into a special
area to ensure that they will not be dispensed.
Facilities should return unacceptable supplies to the district.
Unacceptable supplies returned from the district will be returned to MSD,
during the next MSD delivery.
6)
Store supplies appropriately —See Section VIII, Storing Medicines and
Related Supplies. Remember to store
supplies so that the supplies first to expire are first to be issued (FEFO,
first expiry, first out).
7)
Inform Prescribers and Dispensers of arrival of supplies. These staff member
should be informed so they are aware of the new shipment, particularly if a
product was previously stocked out.
B. The Hospital Level
The
process by which district hospitals, regional hospitals, and referral hospitals
receive supplies from MSD is essentially the same with the following minor
differences. Orders from MSD should be received by the hospital by the end of
the 2 week of the 3rd month of the quarter. The hospital should take
their order directly to the MSD Zonal Store and can pick up the supplies
directly. Otherwise, MSD will deliver
the order to the hospital.
The
sub-HTC should witness the receiving of shipments in accordance with their
responsibilities as specified in the functions of the HTC.

|
Worksheet 9.1: Sample of Good
Receiving Note
|

Total
Session Time: 120 minutes
Prerequisites
·
None
Learning
Tasks
By the end of this session students are expected to be able to:
·
Define Common Terms Used in Stock
Control Of Medicines and Medical Supplies
·
List Stock Control Records and
Documents Used in Physical Inventory
·
Explain the Process of Stock Taking and Reconciliation
·
Explain the Process of Recording and
Reporting the Unserviceable Stocks
Resources
Needed:
·
Flip charts, marker pens, and
masking tape
·
Black/white board, chalk and whiteboard markers
·
LCD projector and computer
·
Handout 10.1: S.F 15 Form
SESSION OVERVIEW
|
Step
|
Time
|
Activity/
Method
|
Content
|
|
1
|
5
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Introduction, Learning Tasks
|
|
2
|
10
minutes
|
Presentation
Buzzing
|
Definitions
of Common Terms Used in Stock Control of Medicines and Medical Supplies
|
|
3
|
10
minutes
|
Presentation
Brainstorming
|
Stock Control Records and
Documents Used in Physical Inventory
|
|
4
|
40
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Process of Stock Taking and
Reconciliation
|
|
5
|
45
minutes
|
Presentation
Small
Group Discussion
|
Process
of Recording and Reporting the Unserviceable Stocks
|
|
6
|
5
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Key
Points
|
|
7
|
5
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Evaluation
|
SESSION
CONTENTS
STEP
1: Presentation of Session Title and Learning Tasks (5 minutes)
READ or ASK students to read the learning tasks and clarify
ASK
students if they have any questions
before continuing
STEP 2: Definitions of Common Terms Used in Stock
Control of Medicines and Medical Supplies (10 minutes)
|
Activity: Buzzing (5 minutes)
ASK students to pair up and buzz on
the following question for 2 minutes
o
Inventory?
o
Lead time?
o
Pull system?
o
Push system?
o
Re order level?
o
Buffer stock?
o
FEFO?
o
FIFO?
o
Stock taking?
o
Unserviceable stock?
ALLOW few pairs to respond and let
other pairs to add on points not mentioned
WRITE their response on the flip
chart/board
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE by using the content below
|
·
Terms Commonly Used in Stock Control
of Medicines and Medical Supplies include;
§ The stock on hand at any
given time
§ The time interval between
when new stock is ordered and when it is received and available for use
§ In a pull system,
quantities to be issued are determined by personnel who receive the supplies
§ In a push system,
quantities to be issued are determined by personnel who issue the supplies
§ Is the level of stock
when you place an order
- Buffer stock/Safety stock
§ I s a stock used during
lead time
§ First expiry first out
§ First in first out
§ Is a process of counting
physically
§ This include products
with one or more of the following characteristic, expired, damaged, has contaminated items, has items instituted for recall,
un repairable or obsolete for medical equipment’s and prohibited
STEP 3: Stock Control Records and Documents Used in
Physical Inventory (10 minutes)
|
Activity: Brainstorming (5 minutes)
Ask students to brainstorm on the
following question:
- What
are the stock control records and documents used in physical inventory?
ALLOW few students to respond
WRITE their responses on the flip
chart/ board
CLARIFY and SUMMARISE by using the content below
|
·
Common stock control records and documents used in
physical inventory include:
- Ledger
books
- Bin cards
- Stock taking sheets

STEP 4: Process of Stock Taking and Reconciliation (40
minutes)
Checking the Stock
The store
keeper makes a physical count of the stock, and makes an entry on the card. The
stock check can be done on the routine basis for all stock (e.g. Once a month)
It is better
if the stock count is done without looking at any other stock information and
then any differences can be investigated later.
To calculate
the theoretical balance which should be present, the formula used
Theoretical
Balance = Opening balance – Stock Issued + Stock Received
If stock
count and theoretical balance agree, then the stock is said to be reconciled
If the stock
count and theoretical balance do not agree, then the stock is not
reconciled
When the
stock is not reconciled, that is when there is a difference between the stock
count and the theoretical balance, it is vital to investigate the reasons for
the difference. There may be a simple explanation (accidental breakage),but it
may be that there is some theft or pilfering occurring, and if this is so, then
random and unannounced spot checks on the stock balance should be made.
STEP 5: Process of Recording and Reporting the
Unserviceable Stocks
(45
minutes)
|
Activity: Small Group Discussion (
20 minutes)
DIVIDE students into small manageable groups
ASK
students to discuss on the
following question
·
What are the
processes of recording and reporting the unserviceable stocks?
ALLOW students to discuss for 20 minutes
ALLOW few groups to present and the rest to add points not mentioned
  Refer students to Handout
10.1: S.F 15 for Further Reading Refer students to Handout
10.1: S.F 15 for Further Reading
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE
by using the contents below
|
- Health facilities should
conduct inspection and physical inventory for their medical stores monthly.
- During the inspection and
physical inventory the medical stores in charge should look for the
following criteria that may render the product unserviceable
o Expiry
o Damage
o Contaminated
items
o Items
instituted for recall
o Un
repairable or obsolete medical equipment
o Prohibited
- Any item deemed to be unserviceable
should be separated from usable items, removed from normal stores ledger
and recorded into the Unserviceable goods ledger.
- A separate marked area should
be identified. All unserviceable medical stores should be in an identified
separate marked area For easy access and verification
- All health facilities in
charges with unserviceable medical stores should report to the District
Medical officer’s (DMO) office using form S.F 15(Refer below) and should ensure that these
products are submitted to the DMO’s office every quarter by the 10th
day of the next quarter through reliable means of transport.
- Facilities in charges should
liaise with the DMO’s office for the most efficient method of
submitting S.F 15 and if possible delivery of unserviceable medical stores
to the DMO’s office.
- Issuance of unserviceable
medical stores should be through the use of local issue voucher
- For pharmaceuticals the
facility in charge should initiate the redistribution of all products that
will not be dispensed by the facility within the next three months to the
nearby facility within the council as per laid out procedures to avoid
expiries.
NOTE: This process is carried out at all
levels of health facilities, i.e. dispensaries/health centres, District
Hospitals, Regional referral hospitals, Special hospitals, zonal hospitals, and
National hospital. The difference lies at the reporting centre (District,
region or Accounting officers) and the personnel reporting.

 Refer students to Handout 10.1:
S.F 15 for Further Reading
Refer students to Handout 10.1:
S.F 15 for Further Reading
STEP 6: Key Points (5 minutes)
Terms
commonly used in stock control of medicines and medical supplies include inventory, lead time, pull system, push system, re order level, buffer
stock etc.
- Stock
control records and documents used in physical inventory are Ledger
books, Bin cards and stock taking sheets
- During the inspection and
physical inventory the medical stores in charge should look for the
following criteria that may render the product unserviceable
o Expiry
o Damage
o Contaminated
items
o Items
instituted for recall
o Un
repairable or obsolete medical equipment
o Prohibited
STEP 7: Evaluation (5 minutes)
- What are common terms used in
stock control of medicine and medical supplies?
- What
are the stock control records and documents used in physical inventory?
- What are the processes of recording
and reporting the unserviceable stocks?
- Which criteria
are used to render a product unserviceable
Reference
Management Science for Health and World Health Organization.
(1997). Managing Drug Supply, (2nd
ed.).West Hartford, Connecticut, USA: Kumarian Press
Ministry
of Health and Social Welfare (2013) Guidelines
for Management of
Unserviceable Medical Stores in
Health Facilities Tanzania Mainland,
Dar-
Es-Salaam
W.H.O (1991) Guidelines on the Storage of Essential Drugs in Eastern and Southern
Africa

|
Handout 10.1: Form S.F 15
|
To…………………….
…………………….
Form S.F 15
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA
SCHEDULE OF UNSERVICEABLE STORES
|
Ledger
Folio
|
Quantity
|
Unit
|
Articles
|
Date of issue or approximate
period in use
|
Rate
|
Value
|
Nature of and reason for
unserviceability and recommendations for disposal
|
|
SHs
|
Cts
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTES Signature
of Officer-in- Charge of Stores
A line must be drawn
Immediately beneath the …………………………………………...
Last entry.
In the case of allocated
Date……………………………………….
Stores the original rate
And value are required
Total
Session Time: 120minutes
Prerequisites
·
None
Learning
Tasks
By the end of this session students
are expected to be able to:
·
Define Handing Over of a Store
·
Explain the Importance of Handing
Over of the Store
·
Explain the Process of Handing Over
of the Store
·
List Stock
Records Documents Used in
Handover of a Store
Resources
Needed:
·
Flip charts, marker pens, and
masking tape
·
Black/white board, chalk and whiteboard markers
·
LCD projector and computer
·
Worksheet
11.1Handover Note
SESSION OVERVIEW
|
Step
|
Time
|
Activity/
Method
|
Content
|
|
1
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Introduction, Learning Task
|
|
2
|
10
Minutes
|
Presentation
Buzzing
|
Definition
of Handing
over of a Store
|
|
3
|
30
minutes
|
Presentation
Small
group discussion
|
Importance of Handing Over of the
Store
|
|
4
|
60
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Process of
Handing Over of the Store
|
|
5
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Stock
Records Documents Used in Handover
of a Store
|
|
6
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Key
Points
|
|
7
|
05
minutes
|
Presentation
|
Evaluation
|
SESSION
CONTENTS
STEP1:
Introduction, Learning Tasks (5 minutes)
READ or ASK students to read the learning tasks and clarify
ASK
students if they have any questions
before continuing
STEP 2: Definition of Handing Over of a
Store (10 minutes)
|
Activity: Buzzing (5 minutes)
Ask students to pair up and buzz on
the following question for 2 minutes:
- What
is handover of a store?
ALLOW few students to respond
WRITE their responses on the flip
chart/ board
CLARIFY and SUMMARISE by using the content below
|
·
Handing
over is the process of transferring of key issue, tasks and changes in
Management plan from one care professional to another.
·
Handover
Notes are documents created by staff members who are about to leave their
position, or permanently to assist their successor to carry out their duties.
STEP
3: Explain the Importance of Handing Over of the Store(30 minutes)
|
Activity: Small Group Discussion (
15 minutes)
DIVIDE students into small manageable groups
ASK
students to discuss on the
following question
·
What are the
importance of handing over a store?
ALLOW students to discuss for 10 minutes
ALLOW few groups to present and the rest to add points not mentioned
CLARIFY and SUMMARIZE
by using the contents below
|
- The importance of the handing over report enable to
prepare scope of duties to be performed is vast for their position.
- The report also helps the newly joined person to
understand the Safety and General condition of the working place.
- The report assists in understanding the documentation
of pharmaceutical records.
- It helps the new joiner to plan his work accordingly.
- It helps the person to understand the average
consumption of each item in a store
- A handing over report can also be used as a reference
if an officer is stuck while performing a job, as details of duties
STEP 4: Process in Handing Over of the Store
(60minutes)
·
In charge of the store is accountable for the
safekeeping of the stock in hand. Hence,
should be required to conduct stocktaking exercises at specified intervals. If
there is a change of staff, both the incoming and outgoing stores officers are
recommended to take the following steps
- All items held in stock should be checked to
ensure they tally with the records.
- If it is not practicable to check all items
during the handover, the incoming officer should select randomly a number
of items for checking, particularly those of high value.
- Any
surpluses or shortfalls of items identified should be documented and
reported to senior officers.
- The outgoing and incoming officers should sign
a handover report for record purposes
 Refer students to work sheet
11.1: filling handover note.
Refer students to work sheet
11.1: filling handover note.
STEP
5: List Stock records and documents
used in Handover of a store
(5 minutes)
- Bin cards
- Ledger book
- Requisition book
- Issue voucher
- Job description
- Handover note
STEP 6: Key Points (5 minutes)
- Handing over is the process of transferring of key
issue, tasks and changes in Management plan from one care professional to
another.
- Importance of handing over include to help the newly
joined person to understand the Safety and General condition of the
working place, to help the new joiner to plan his work, to help the person
to understand the average consumption of each item in a store accordingly,
etc
- Stock records and documents used in Handover of a store
includebin cards, ledger book, requisition book, issue voucher, job
description and handover note
STEP 7: Evaluation (5 minutes)
·
What is handover of a store?
·
What are the
importances’s of handing over a store?
·
What are the steps in handing
over of the store?
References
Management Science for Health and World Health Organization.
(2012). Managing Access to Medicines and
Health Technology, (3rd ed.). Kumarian Press
Management Science for Health and World Health Organization.
(1997). Managing Drug Supply, (2nd
ed.).West Hartford, Connecticut, USA: Kumarian Press
World Health Organization (WHO), Regional Office for Africa
Brazzaville 2004, Management of Drugs
at Health Centre Level Training Manual.
Shirima, L. L (1988): Basic Store-keeping and Warehouse
Management. General Publication United Republic of Tanzania, Public Procurement Act, 2004, Dar es
Salaam
Jessop, D and Morrison (1994) Storage and Supply of Materials,
6th Edition, Prentice Hall
Laurie L, Editor, (2003) Guidelines
for the Storage of Essential Medicines and Other Health Commodities. John Snow,
Inc. /DELIVER in collaboration with the World Health Organization

|
Worksheet 11.1:.Handover Note
|
|
Instructions
: filling handover note
|
Handover Note
Template
Name: Index
number:
Job
Title:
Date
of Handover Note:
Duration
of Assignment (include start and end date):
Brief
Description of Duties:
This section may be kept brief when
up-to-date terms of reference (TOR) are attached.
Supervisor
and reporting procedures:
Regular/re-occurring
meetings, reports or procedures:
Key
Documents/reference material to read (attach when possible):
Status
of recent and current projects/reports/meetings:
- Name of project/report/meeting
- Status
- Action needed
- Partners
- Budget (if applicable)
- Critical issues/challenges/priorities
- Repeat as many times as necessary. Indicate priority
projects.
Where
to find files (hardcopy and electronic):
Calendar
of major activities and/or events (optional):
Contacts
(internal and external):
|
Name
|
Organization
|
Phone
|
E-mail
|
Comments
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Your
contact information after departure:
Phone
Email




















